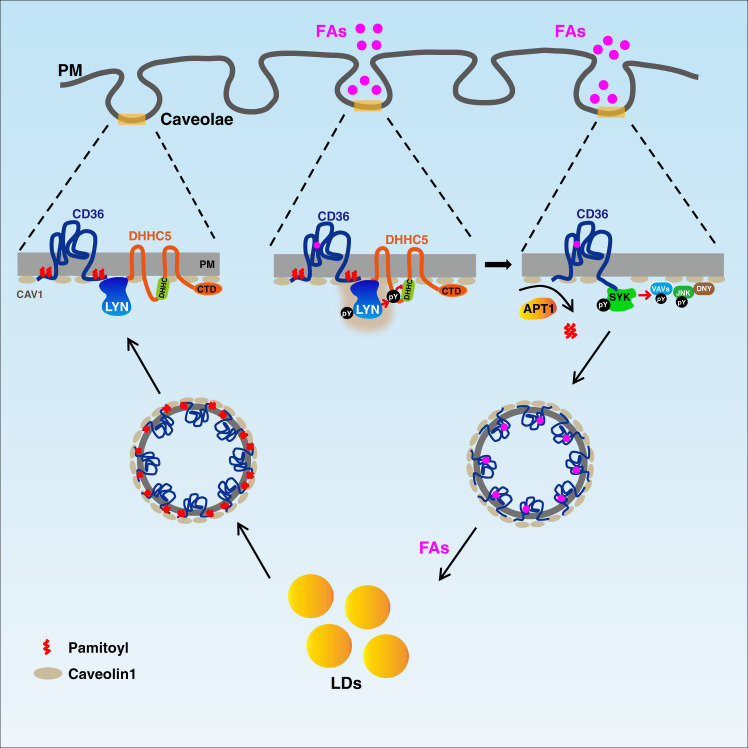
Fig. 8. A working model of FA uptake by CD36-mediated caveolar endocytosis.
The plasma membrane of adipocytes is enriched with caveolaes. In a caveolae, CD36 is in the palmitoylated form and its FA binding cavity is on the outer layer, whereas CAV1 is on the inner layer. When FAs bind to CD36, a SRC kinase LYN gets activated, and it phosphorylates DHHC5 at Tyr91 and inactivates DHHC5, resulting in the subsequent depalmitoylation of CD36 by the depalmitoylase APT1. The depalmitoylated CD36 then recruits SYK to phosphorylate VAV and JNK, thereby initiating CD36-mediated caveolar endocytosis. The endocytosed vesicles deliver FAs to lipid droplets for storage. After that, CD36 gets re-palmitoylated and recycled to the plasma membrane for another round of delivery.