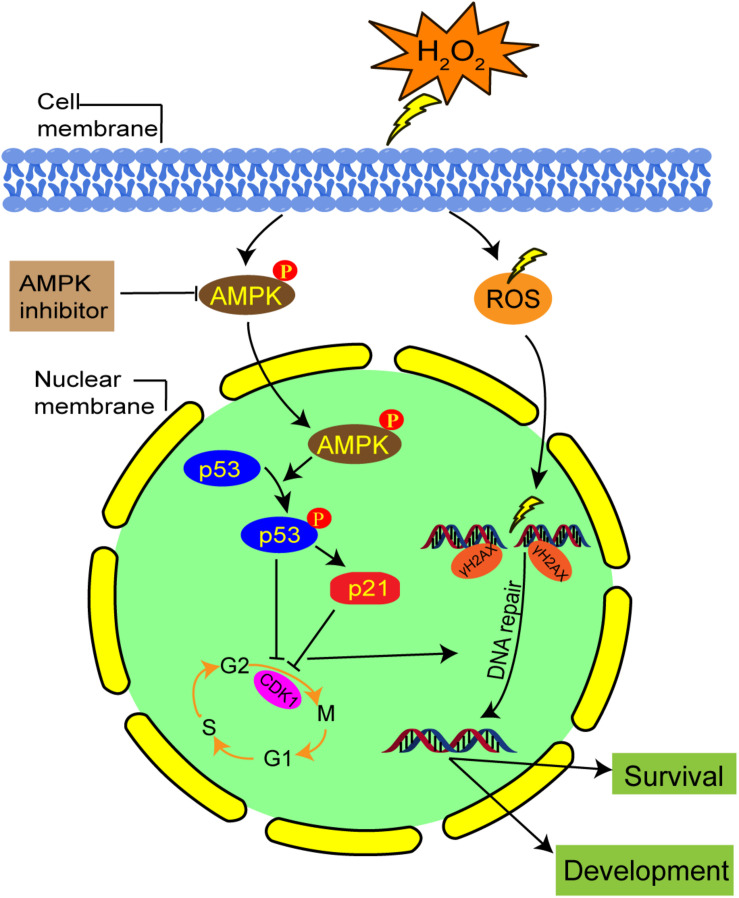
FIGURE 8.
Schematic representation of the AMPK-mediated G2 arrest regulation and DNA damage in mouse zygotes under mild oxidative stress. Oxidative stress activated AMPK first in the cytoplasm, which is subsequently translocated in the nucleus. AMPK activation contributes to oxidative stress-induced G2 arrest, by inhibiting CDK1 activity via the upregulation protein level of p53 and p21. The G2 arrest facilitates DNA damage repair and the development and survival of oxidative stress-damaged embryos.