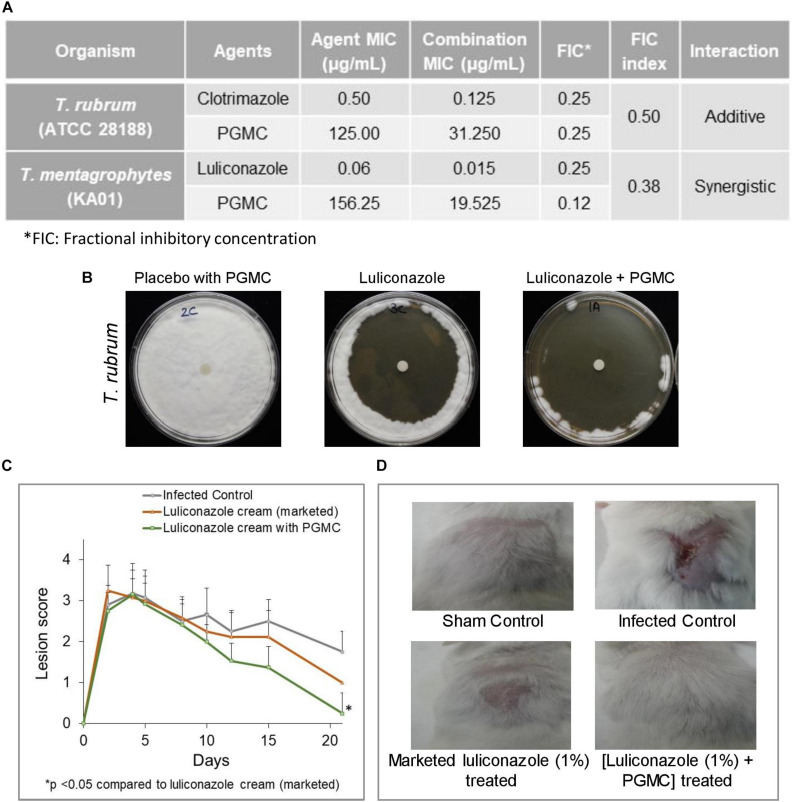
FIGURE 6.
Efficacy of PGMC in combination with various antifungal agents against Trichophyton spp. (A) Combination effect of PGMC and antifungal agents against drug susceptible Trichophyton rubrum (ATCC 28188) and resistant Trichophyton mentagrophytes var interdigitale (KA01). determined through checkerboard assays. (B) Representative images of in vitro zone of inhibition assays using topical formulations containing no antifungal agent (placebo cream with PGMC), marketed formulation containing 1% luliconazole and formulation containing 1% luliconazole plus PGMC against Trichophyton rubrum (C) Efficacy of luliconazole (1%) formulations in a murine tinea infection model. Left panel showing effect of luliconazole formulation containing PGMC on skin lesion in a Trichophyton mentagrophytes (ATCC 24953) infected mouse model. Infection was initiated on Day 0 and treatment was started on Day 5 post infection and continued till Day 14. The data is represented as mean ± SD (n = 4). Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test (∗p < 0.05). Topical luliconazole formulation containing PGMC showed significant (p < 0.05) antifungal effect relative to marketed formulation of 1% luliconazole (21 days post infection). (D) Representative pictures of lesions on mouse skin on day 21 in the tinea infection model.