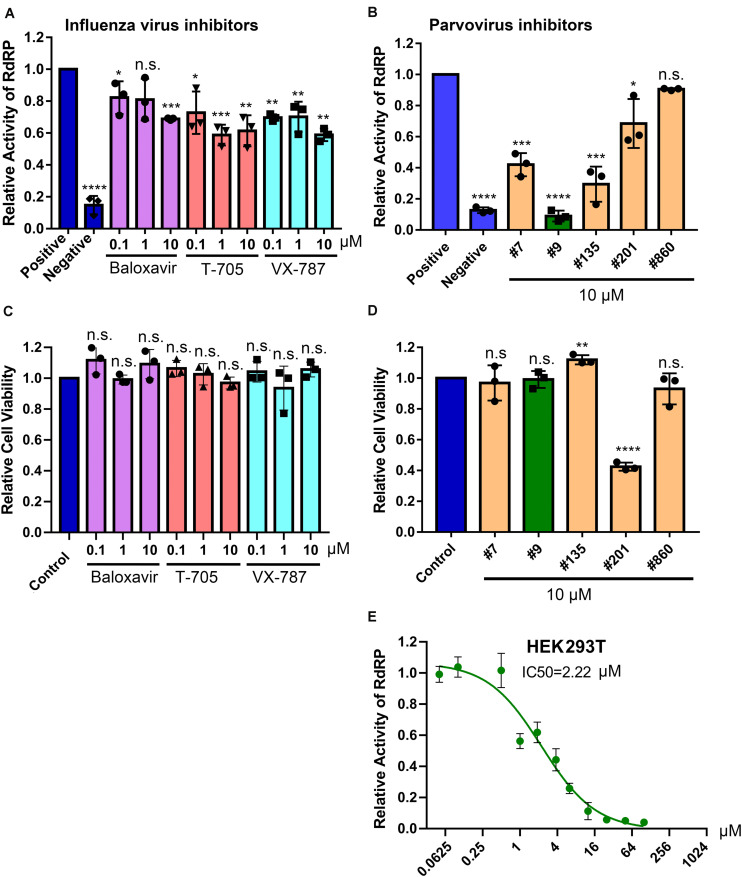
FIGURE 6.
Screening of BRBV RdRP inhibitors using the BRBV replicon luciferase reporter. (A,B) Inhibition of RdRP activity. The inhibitory effect of different drugs, inhibitors targeting RdRP of influenza virus (Flu inhibitors) (A) and inhibitors of anti-parvovirus endonuclease compounds (Parvovirus inhibitors) (B), on BRBV RdRP activity was quantified using the GP-gLuc reporter assay at different concentrations as indicated. DMSO was used as a positive control of the reporter (Positive), and transfection with only pcDNA-PB1, PB2, and NP was used as a negative control of the reporter (Negative). At 3 days post-transfection, the activity of the expressed Gaussia luciferase was quantified using a Gaussia Luciferase Glow Assay Kit (Pierce). Results from each compound were normalized to the vehicle control in each experiment and were expressed with the means and standard deviations obtained from three experiments performed in duplicate. (C,D) Cytotoxicity assay. Compounds were assayed for cytotoxicity in HEK293T cells at the concentrations indicated using a CytoTox-GloTM Cytotoxicity Assay kit (Promega). The results are normalized to the mock-treated control (set as 1.0). Values are the means and standard deviations obtained from three experiments, each performed in duplicate. (E) IC50 of compound #9 on RdRP activity. Compound #9 was applied to HEK293T cells transfected with the gLuc reporter system of five plasmids at various concentrations as indicated. The polymerase activity was quantified by measuring the luciferase activity. Values are the means with standard deviations and are normalized to the mock group from three experiments performed in duplicate. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated with GraphPad Prism software. P values are calculated using one-way and Tukey–Kramer post-test, compared with DMSO or mock control. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; and n.s. (P > 0.05) denotes no statistical significance.