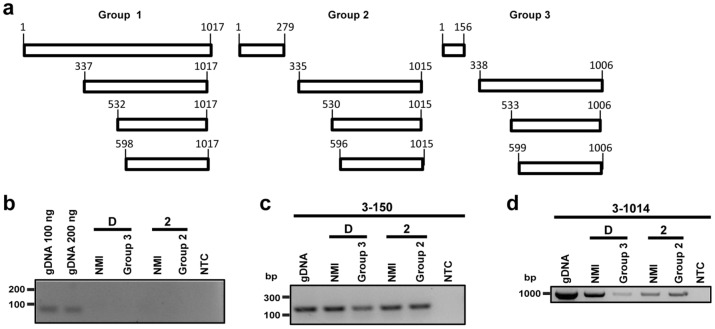
Figure 5.
Determination of ankG variant transcripts. (a) Schematic overview of possible transcripts of the three different AnkG groups is shown. The first group is represented by NMI, the second group by 19/34, and the third group by Z3574-1/92. The numbers of the first base pair of potential internal start codons are given, which are in frame with the stop codon at base pair position 1,015–1,017 (group 1), 1,013–1,015 (group 2) or 1,004–1,006 (group 3). (b) DNase treated RNA was analyzed for DNA contamination using dotA specific primers. As positive control C. burnetii NMII gDNA was used in different amounts. Gel electrophoretic analysis was performed using a 2% agarose gel. (c, d) Gel electrophoresis image of the different ankG mRNA sections probed in the distinct C. burnetii strains. gDNA served as positive control, while the non-template control (NTC) contains only water. RNA was isolated from all axenically grown strains (2—grown in ACCM-2; D—grown in ACCM-D), reverse-transcribed in cDNA, and amplified by PCR. Gel electrophoretic analysis was performed using a 2% agarose gel. The cDNA was analyzed for the presence of (c) the mRNA region encoding the N-terminal part of the protein (base pairs 3–150) and (d) the full-length transcript (base pairs 3–1,014).