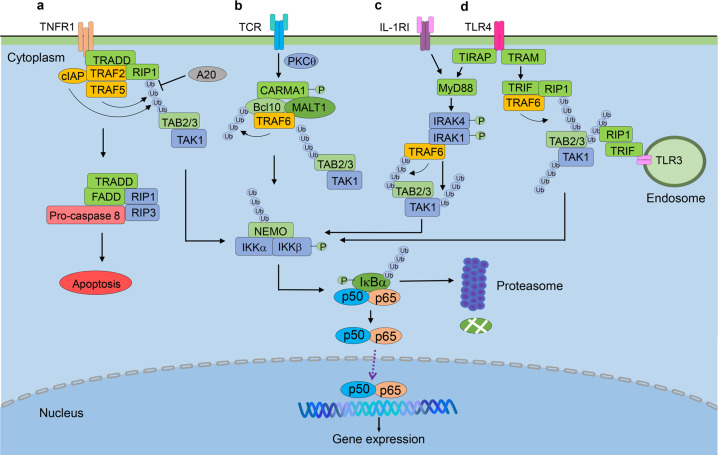
Fig. 1.
Activation and regulation of canonical NF-κB pathway. a Ligation of TNFR leads to the recruitment of TRADD and interaction of the E3 ubiquitin ligases cIAP1/2, TRAF2 with the protein kinase RIP1. RIP1 then is K63-ubiquitinated and recruited to NEMO, resulting in the formation of the TAK1-IKK complex. TAK1 phosphorylates and activates IKKβ that in turn induces the phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα, allowing NF-κB dimers to translocate to the nucleus and drive the transcription of the target gene. b TCR stimulation induces canonical NF-κB activation through the CARD11/Bcl10/MALT1 (CBM) complex. Upon stimulation, CARD11 (CARMA1) is recruited and phosphorylated by PKC-θ, leading to the recruitment of Bcl10 and MALT1 to form the CBM complex. MALT1 then recruits TRAF6, which mediates K63 ubiquitination of itself and Bcl10, followed by the activation of TAK1 and IKK-mediated canonical NF-κB activation. c, d TLR and IL-1RI mediate signal transduction through MyD88. TLR4 recruits TIRAP and TRAM, which recruits MyD88 and TRIF, respectively, and IL-1RI recruits MyD88 directly. MyD88 induces the recruitment of IRAK1 and IRAK4, which further recruit TRAF6 to activate TAK complex and downstream signaling pathways. The activity of canonical NF-κB is regulated at multiple levels. The expression of A20 is activated by NF-κB, which deubiquitinates RIP1, TRAF6 and NEMO to destabilize the IKK complex. TRADD, TNF-R-associated death domain; RIP1, receptor-interacting protein 1; cIAP1/2, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 and 2; TRAF2/5, TNF-R-associated factor 2 and 5; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator; TAK1, TGF-β-activated protein kinase 1; IKKβ, inhibitor of κB(IκB) kinase β; TCR, T cell receptor; PKC-θ, protein kinase C-θ; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; TIRAP, Toll/IL-1 receptor adaptor protein; TRAM, TRIF-related adaptor molecule; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon beta; IRAK-1/4, IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 and 4