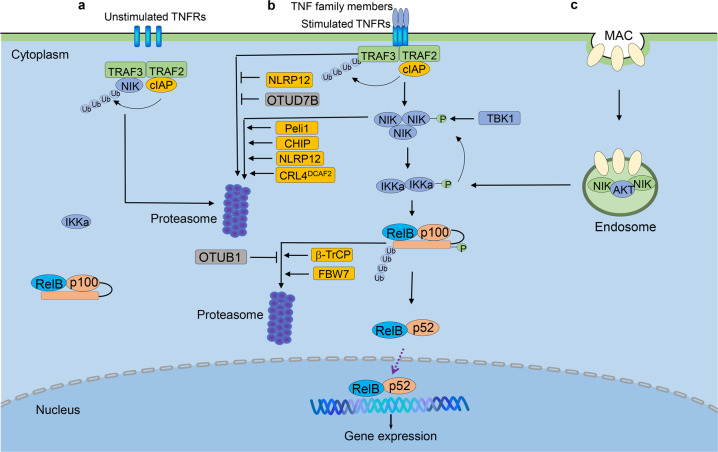
Fig. 2.
Regulation of non-canonical NF-κB pathway. a In steady-state, newly synthesized NIK is targeted for ubiquitination-dependent degradation mediated by the cIAP-TRAF2-TRAF3 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, which prevents NIK accumulation and non-canonical NF-κB activation. b Ligation of specific TNFR superfamily members by their ligands (TNF family members) induces the recruitment of TRAF3-TRAF2-cIAP to the receptor complex, followed by K48 ubiquitination and degradation of TRAF3, resulting in stabilization and accumulation of NIK. NIK, together with IKKα, mediates p100 phosphorylation and ubiquitination-dependent process, to generate p52 and allow p52-RelB heterodimer to enter the nucleus for target gene transcription. c Activation of non-canonical NF-κB by MAC involves the formation of an endosome-based signaling complex containing NIK, AKT and MAC. AKT mediates NIK stabilization and IKKα phosphorylation and activates downstream non-canonical NF-κB. Non-canonical NF-κB is negatively regulated through TRAF3 deubiquitination mediated by OTUD7B and degradation of NIK mediated by IKKα, TBK1, CHIP, NLRP12, Peli1 and CRL4DCAF2. NIK, NF-κB-inducing kinase; TRAF3, TNFR-associated factor 3; TRAF2, TNFR-associated factor 2; CHIP, carboxyl terminus of HSC70-interacting protein; NLRP12, nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich-repeat containing proteins 12; cIAP1/2, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 and 2; MAC, complement membrane activation complex