Fig. 3.
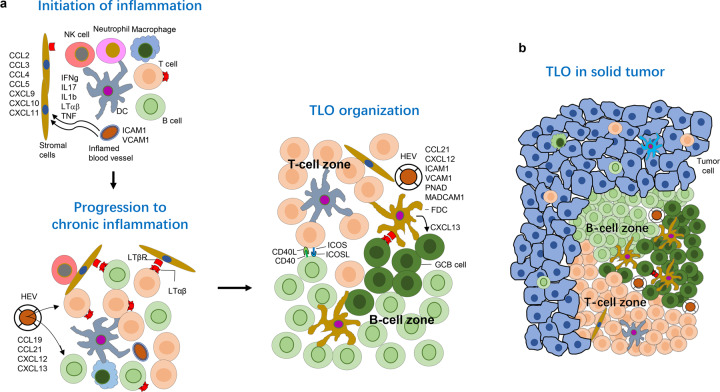
The function of non-canonical NF-κB in lymphoid tissue development and tumor immunology. a The inflammatory microenvironment provides the initial signal for TLOs neogenesis. At sites with inflammation, initiated by various innate immune cells (such as macrophages and DCs), various chemokines and cytokines are produced, leading to the recruitment of lymphocytes. The local high endothelial venule (HEV) secrets adhesion molecules VACAM-1, ICAM-1, and MadCAM-1. The lymphocytes interact with local stromal cells, particularly through LTα1β2 and its receptor LTβR, which induces the expression of various chemokines, such as CXCL12, CXCL13, CCL19, and CCL21. Together, these chemokines and adhesion molecules, as well as local stromal cells and FDCs, recruit lymphocytes from nearby HEVs and govern their organization into T-cell and B-cell zones that contain GC. b The schematic diagram shows a TLO located within a solid tumor with a T cell zone containing mature DCs and FRCs as well as a B cell zone with GC-B cells and FDCs. DCs, dendritic cells; TLOs, tertiary lymphoid organs; GC, germinal center; FDCs, follicular DCs; FRC, fibroblastic reticular cells