Figure 9.
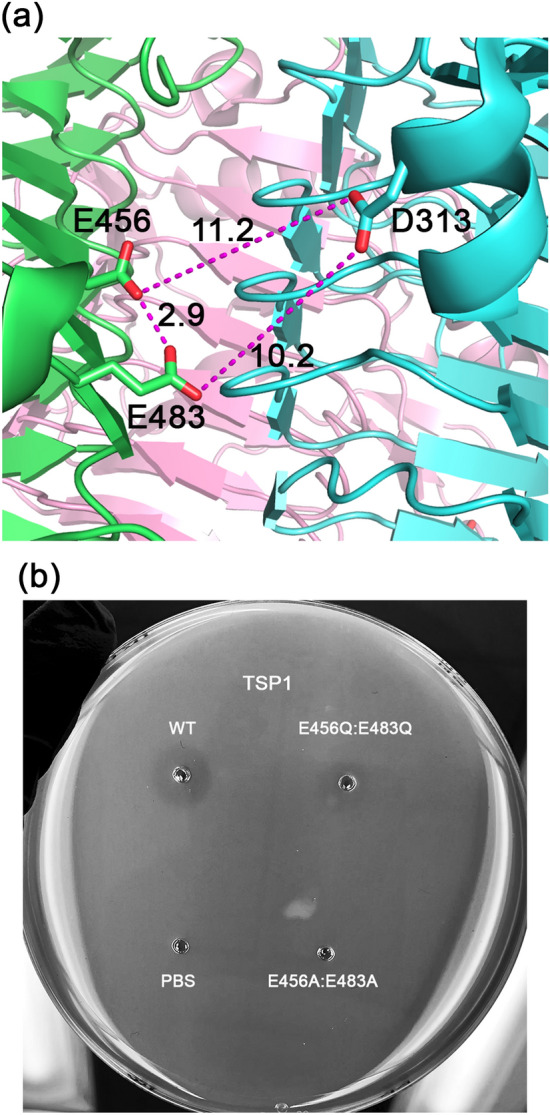
TSP1 active site structure and halo assay of active site residues. Structure and mechanism-based analyses were used to identify the active site residues. (a) Depiction of key carboxylic acid residues in the interface between two TSP1 subunits. The figure was generated using the computer program PyMol v1.8.0.2 (Schrödinger, LLC, https://www.pymol.org). (b) Halo assay of wild-type and mutant TSP1. E. coli strain ATCC 700728 was embedded in agarose. Wells (3 mm) were cut out of the agarose and loaded with 10 µL (6 mg/mL) of active site TSP1 mutants, and incubated overnight at 37 °C to visualize glycosidase activity. The absence of a halo for E456A:E483A TSP1 suggests an inhibition of enzymatic activity. Alternatively, the appearance of a halo for the E456Q:E483Q mutant indicates TSP1 retains the ability to display glycosidase activity. Wild-type TSP1 and PBS only served as positive and negative controls for glycosidase activity, respectively.
