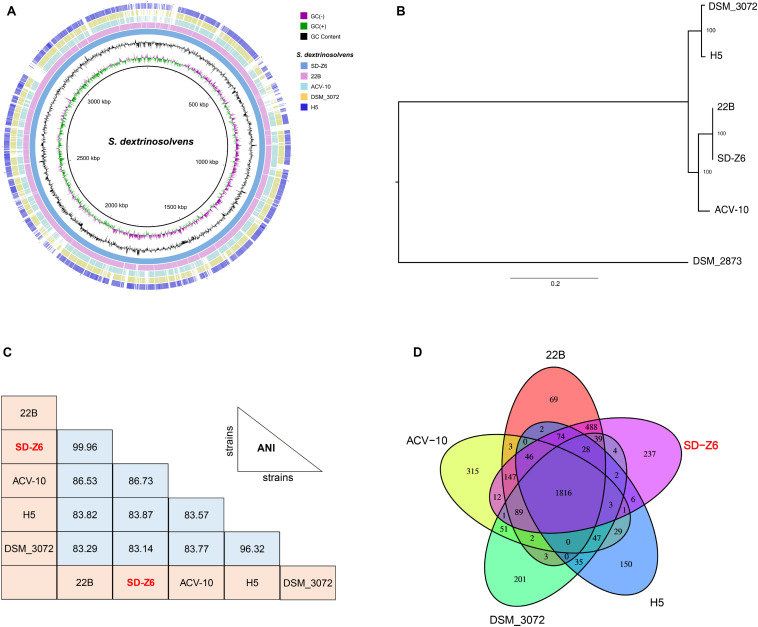
FIGURE 2.
Comparative genome analysis of Succinivibrio dextrinosolvens strain Z6 and closely related strains. (A) BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG) analysis of S. dextrinosolvens strain Z6 and the genomes of S. dextrinosolvens 22B, S. dextrinosolvens ACV-10, S. dextrinosolvens H5, and S. dextrinosolvens DSM_3072. The innermost ring represents the skew (- and +), followed by GC content. The third ring shows S. dextrinosolvens strain Z6 (blue), ring 4 S. dextrinosolvens 22B (pink), ring 5 S. dextrinosolvens ACV-10 (light blue), ring 6 S. dextrinosolvens DSM_3072 (yellow), and ring 7 S. dextrinosolvens H5 (dark blue). (B) Phylogenetic tree highlighting the relationship of S. dextrinosolvens strain Z6 with other strains in the Succinivibrio genus. The evolutionary history was inferred using the maximum likelihood method and showed that S. dextrinosolvens Z6 is a member of the Succinivibrio genus. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. Succinimonas amylolytica DSM_2873 is an outgroup. (C) Pairwise comparisons of average nucleotide identity (ANI), and (D) global gene conservation in Succinivibrio. Each oval represents the total number of genes in each genome. Overlapping regions depict the number of genes shared between the respective genomes.