Figure 3.
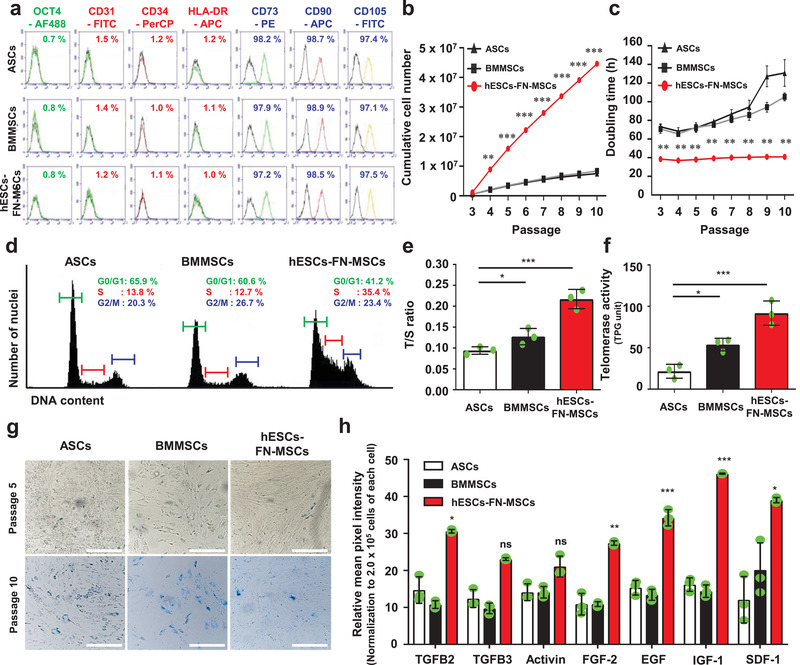
The MSC surface markers of hESC‐FN‐MSCs are similar to both of ASCs and BMMSCs, but hESC‐FN‐MSCs have unique cell behaviors and characteristics. a) Surface antigen profiling with FACS showed that hESC‐FN‐MSCs are similar to ASCs and BMMSCs. OCT4 is a pluripotent marker, while CD73, CD90, and CD105 are positive MSC markers, and CD31, CD34, and HLA‐DR are negative MSC markers. b,c) Upon measuring the cumulative cell number and population doubling time until 10 passages, hESC‐FN‐MSCs showed high proliferative capabilities with short doubling time compared to ASCs and BMMSCs. Interestingly, even at passage 10, hESC‐FN‐MSCs were able to maintain their short doubling time, but ASCs and BMMSCs drastically increased their doubling time. n = 4, mean ± s.d., ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001 versus ASCs and BMMSCs (two‐way ANOVA). d) Representative flow cytometric plot showing the cell cycle analysis of ASCs, BMMSCs, and hESC‐FN‐MSCs at passage 3. A higher number of cells were in the S phase for hESC‐FN‐MSCs compared to both ASCs and BMMSCs. e) Relative telomere length expressed as T/S ratio measured by qRT‐PCR. The relative telomere length of hESC‐FN‐MSCs was longer than those of ASCs and BMMSCs. n = 3, mean ± s.d., * P < 0.05, and *** P < 0.001 (one‐way ANOVA). f) Telomerase activity in hESC‐FN‐MSCs was higher than that in ASCs and BMMSCs. n = 3, mean ± s.d., * P < 0.05, and *** P < 0.001 (one‐way ANOVA). g) Comparison of cellular senescence in ASCs, BMMSCs, and hESC‐FN‐MSCs at passages 5 and 10 by SA‐b‐gal staining. hESC‐FN‐MSCs at passages 5 and 10 showed a low level of senescence compared with ASCs and BMMSCs. Scale bar: 100 µm. h) The amounts of growth factors and cytokines were significantly higher in hESC‐FN‐MSCs than in ASCs and BMMSCs. n = 3, mean ± s.d., * P < 0.05, and *** P < 0.001 versus ASCs and BMMSCs (two‐way ANOVA).
