Figure 1.
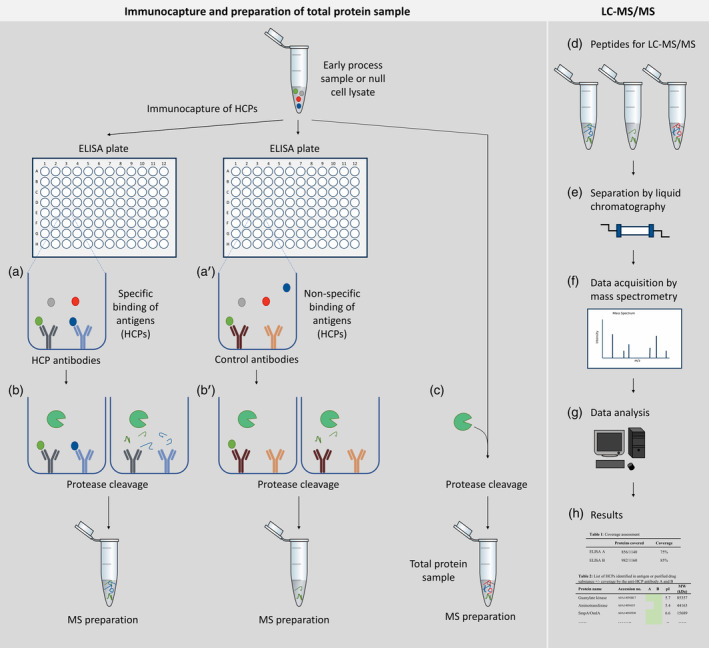
Experimental setup ELISA‐based immunocapture followed by protein identification by LC–MS/MS (ELISA‐MS). Left panel: immunocapture and preparation of total protein sample. For immunocapture, ELISA plates are coated with specific HCP antibodies or control antibodies. Antigen, an early process sample or a null cell lysate, containing HCPs are added to each plate and unbound HCPs are removed during washing steps (a, a'). Bound HCPs are digested in the plate using trypsin (b, b′). An aliquot of the early process sample or null cell lysate is digested under similar conditions in parallel without antibodies (c) and serves as a measurement of total protein content to identify all HCPs (referred to as total protein sample). Right panel: peptides from the immunocapture and the total protein sample are analyzed by LC–MS/MS (d). During LC–MS/MS, peptides are separated by liquid chromatography (e) and data are acquired by mass spectrometry (f). The LC–MS/MS data are searched against a protein sequence database (g) to create resulting protein identification lists for each sample (h). HCPs identified by LC–MS/MS after immunocapture is compared to the total number of HCPs identified in the early process sample or null cell lysate to calculate HCP coverage (h)
