Figure 9.
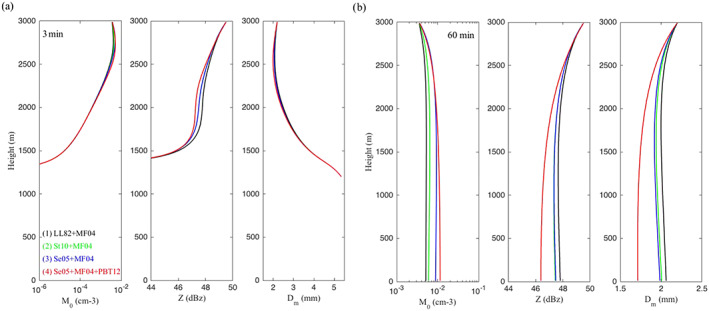
Comparison of vertical profiles of the drop number concentration (M0 in cm−3), radar reflectivity (Z in dBz), and mass‐weighted mean drop diameter (Dm in mm) for one‐dimensional rainshaft simulations using the bin scheme of Prat et al. (2012) with various combinations of coalescence and breakup kernel formulations (with collision‐coalescence, collisional breakup, and sedimentation as the only processes included). The formulations include (1) LL82, MF04 (black), (2) St10, MF04 (green), (3) Se05, MF04 (blue), and (4) Se05, MF04, PBT12 (red). Here LL82 (Low & List, 1982b), MF04 (McFarquhar, 2004), St10 (Straub et al., 2010), Se05 (Seifert et al., 2005), and PBT12 (Prat et al., 2012) are the formulations tested. Results are presented for a total simulated time of (a) 3 min (i.e., transient situation) and (b) 1 hr (i.e., steady state situation). The idealized simulations use an exponential drop SD with a nominal rain rate of 50 mm hr−1 imposed at the top of the model column.
