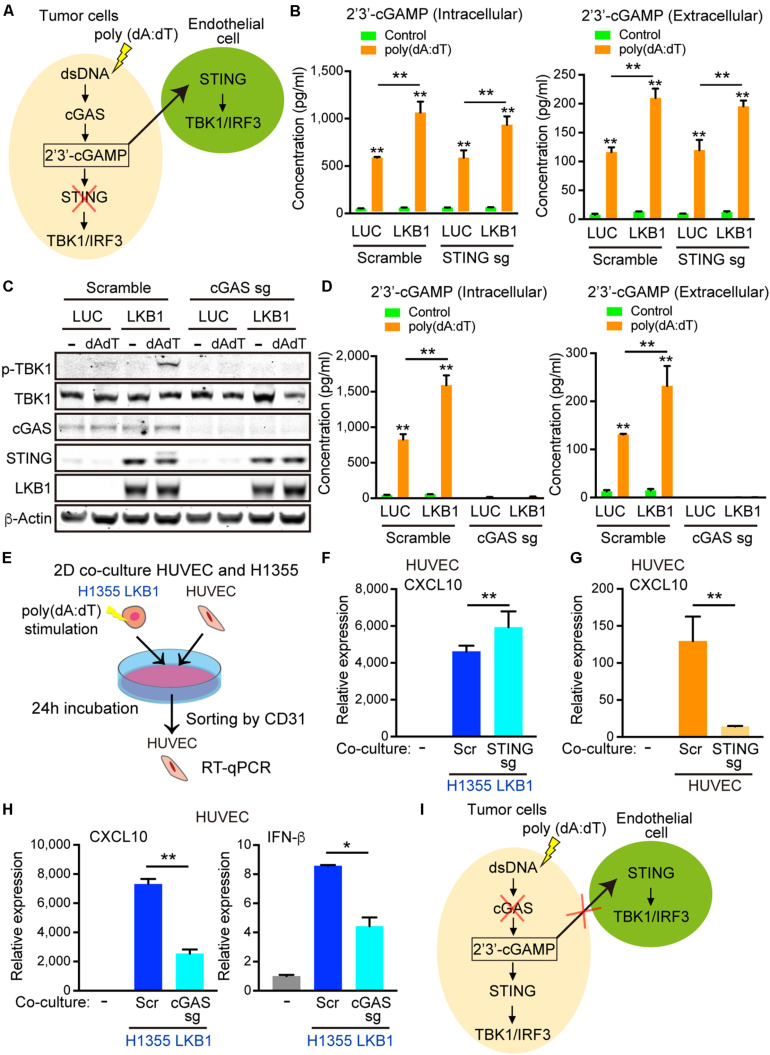
FIGURE 5.
2′3′-cGAMP exported by cancer cells activates STING signaling in endothelial cells. (A) Schematic of cGAS-STING signaling in tumor cells after poly (dA:dT) stimulation and hypothesized export of 2′3′-cGAMP activating STING in the endothelial cells, which would be unaffected by tumor cell STING knockout. (B) Intracellular and extracelluar 2′3′-cGAMP ELISA of transduced LUC and LKB1 H1355 ± scramble or STING knockout. (C) Immunoblot of the indicated proteins in H1355 cells transduced with LUC and LKB1 with scramble or cGAS knockout (cGAS sgRNA) in 2-D culture. (D) Intracellular and extracellular 2′3′-cGAMP ELISA of transduced LUC and LKB1 H1355 with scramble or cGAS knockout. (E) Schematic of the 2-D co-culture experiment and sorting by CD31 + cells. (F) qRT-PCR of CXCL10 of HUVECs after 2-D co-culture with H1355 cells for 24 h with scramble or STING knockout. (G) qRT-PCR of CXCL10 of HUVECs scramble or STING knockout after 2-D co-culture with H1355 cells for 24 h. (H) qRT-PCR of CXCL10 and IFN-β of HUVECs after 2-D co-culture with H1355 cells for 24 h with scramble or cGAS knockout. (I) Schematic of cGAS-STING pathway in tumor cells after poly (dA:dT) stimulation demonstrating that silencing of cGAS impairs accumulation of 2′3′-cGAMP and export from the cells, limiting the STING activation in endothelial cells. P values were calculated by one-way ANOVA, or two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test; **P < 0.01, *0.01 < P < 0.05. Data shown as mean values, error bars ± SD, (n = 3 biological replicates).