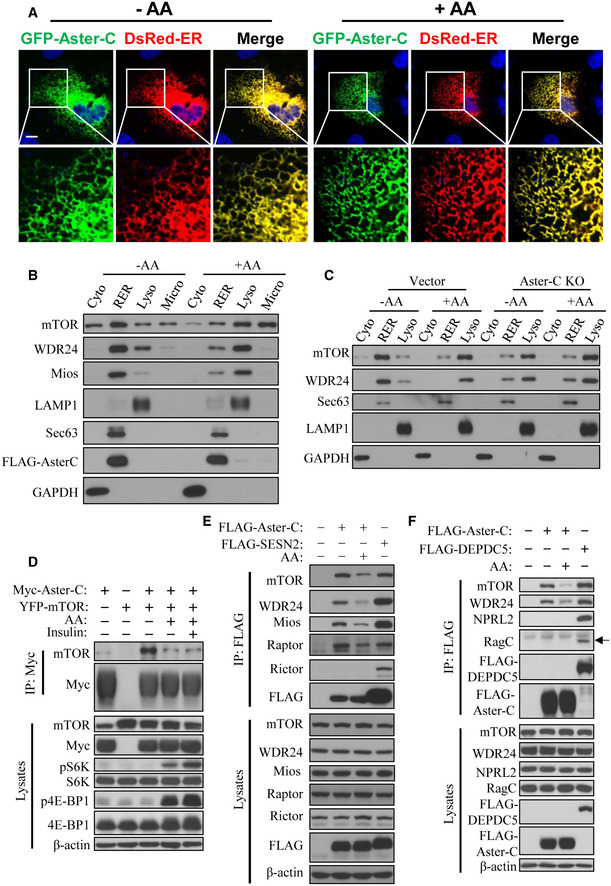
Confocal image analysis depicting the co‐localization of Aster‐C with the ER in C2C12 cells transiently expressing GFP‐Aster‐C and DsRed‐ER under starvation and in response to AA stimulation. Scale bar, 5 μm.
Subcellular fractionation analysis of mTOR, GATOR2 complex, and Aster‐C localization in HEK293T cells transiently expressing FLAG‐Aster‐C under starvation and in response to AA stimulation. LAMP1, Sec63, and GAPDH were used as lysosomal (Lyso), rough ER (RER), and cytosol (Cyto) protein markers, respectively. Microsomal fraction (Micro) was also used in the blot.
Subcellular fractionation analysis of mTOR and GATOR2 complex in C2C12‐Vector and Aster‐C KO cells under starvation and in response to AA stimulation. LAMP1, Sec63, and GAPDH were used as lysosomal (Lyso), rough ER (RER), and cytosol (Cyto) protein markers, respectively.
Co‐IP analysis of the interaction of Aster‐C with exogenous mTOR in response to starvation and AA or insulin stimulation in HEK293T cells transiently expressing the indicated proteins. Anti‐Myc antibody was used for immunoprecipitation.
Co‐IP analysis of the interaction of Aster‐C with endogenous mTOR and the GATOR2 complex using FLAG‐Sestrin2 (SESN2) as a positive control in HEK293T cells transiently expressing the indicated proteins. Anti‐FLAG antibody was used for immunoprecipitation.
Co‐IP analysis of the interaction of Aster‐C with mTOR, the GATOR2 complex, GATOR1 complex, and the Ragulator‐Rag complex using FLAG‐DEPDC5 as a positive control in HEK293T cells transiently expressing the indicated proteins. Anti‐FLAG antibody was used for immunoprecipitation. Black arrow indicates the RagC protein.
Data information: Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.