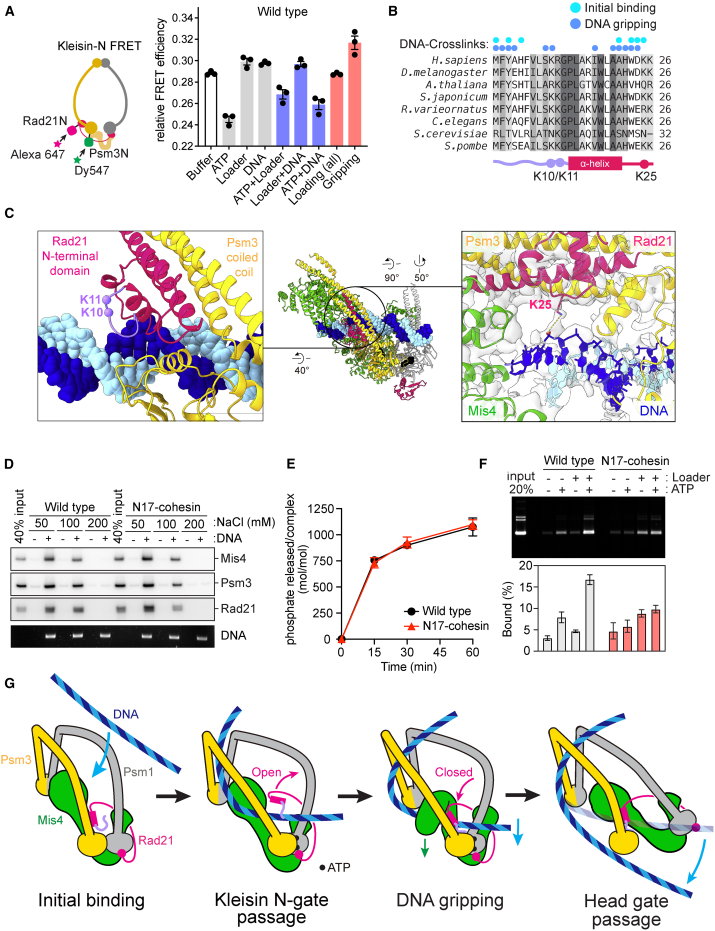
Figure 7.
A Kleisin N-terminal Tail Guides DNA into the Cohesin Ring
(A) Schematic of the kleisin N-gate FRET construct. FRET efficiencies at the kleisin N-gate were recorded under the indicated conditions using a 3-kb plasmid DNA as a substrate. ADP⋅BeF3− was used in the gripping incubation. Results from three independent repeats and their means and standard deviations are shown.
(B) Sequence alignment of the cohesin N-tail. Positions of DNA crosslinking in the initial binding and the DNA gripping state are indicated.
(C) Atomic model of the Rad21 N-tail (left), showing the conserved K10 and K11 residues relative to the DNA. A magnified view around K25 is also shown (right), including the cryo-EM density.
(D) Comparison of WT and N17-cohesin in a DNA gripping experiment. Following reaction with a bead-bound DNA loop substrate and washes, the bead-associated proteins and DNA were analyzed by immunoblotting and gel electrophoresis.
(E) Comparison of ATP hydrolysis by WT and N17-cohesin in the presence of the loader and a 3-kb plasmid DNA. Shown are the means and standard deviations from three independent experiments.
(F) Loading of WT and N17-cohesin onto a 3-kb plasmid DNA. Following the loading reaction, cohesin was immunoprecipitated and washed with buffer containing 750 mM NaCl, and recovered DNA was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Shown are the means and standard deviations from three independent experiments.
(G) A model for DNA entry into the cohesin ring. The kleisin N-tail guides DNA through the kleisin N-gate before DNA reaches the ATPase heads. ATP hydrolysis and passage through the head gate completes DNA entry.
See Figure S7 for further analyses of the kleisin N-tail and Video S1 for an animated model of DNA entry into the cohesin ring.