Fig. 15.2.
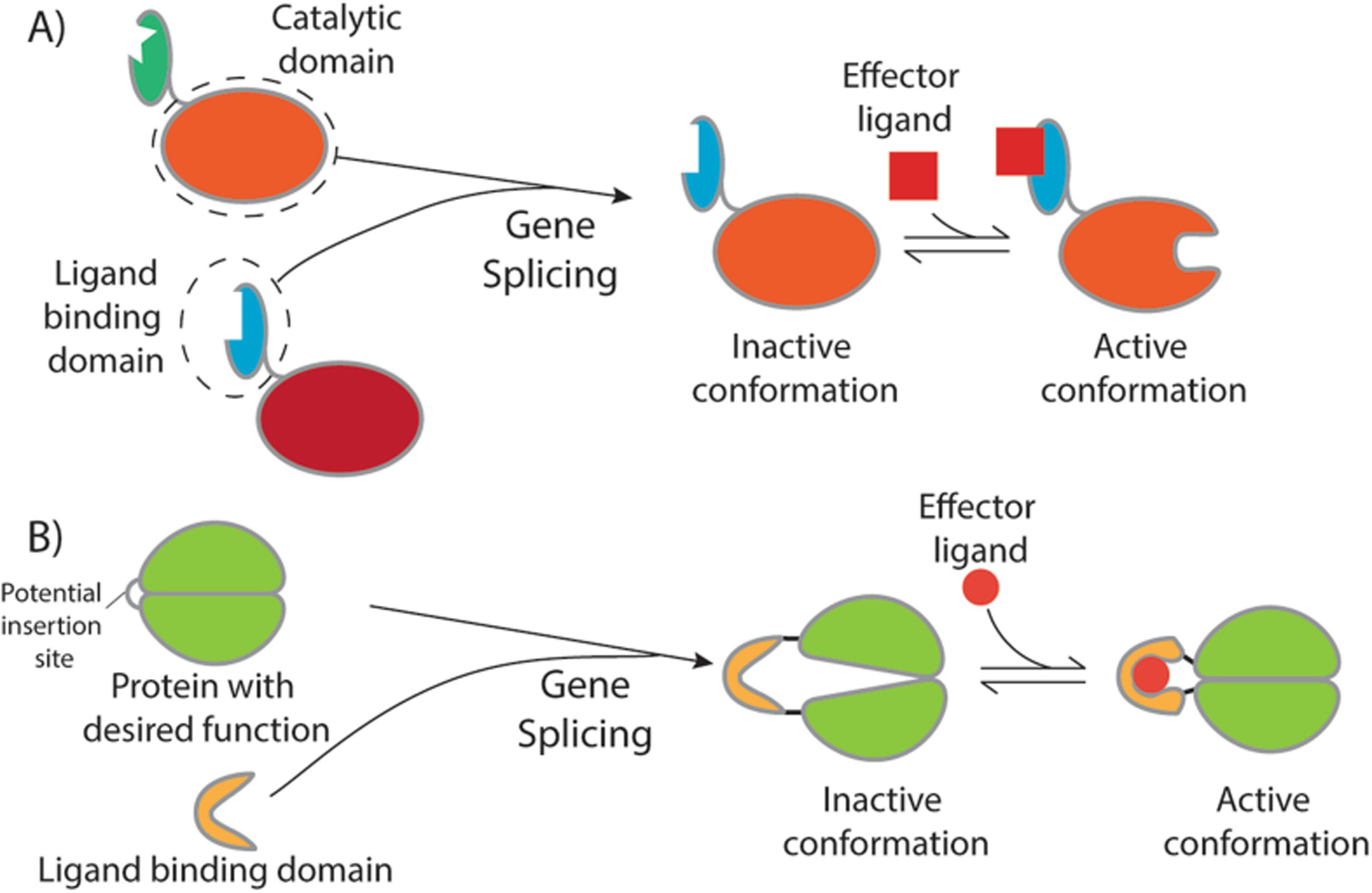
Methods of rational domain insertion. (a) Homologous proteins with catalytic domains are often structurally similar enough that regulatory domains sensitive to different effectors can be swapped or added to homologs without a regulatory domain, as in the above example where the blue regulatory domain is spliced onto the orange catalytic domain. (b) In cases where the protein with the desired function does not have any allosteric homologs, a conditionally disordered linker that becomes ordered in response to environmental changes or a regulatory domain can be inserted into the middle of a loop in the host protein sequence. In this example, the green enzymatic domain is inactive when the yellow regulatory domain is in its open apo conformation. Once the regulatory domain binds its effector ligand, it adopts a conformation that allows the enzymatic domain to adopt its active conformation
