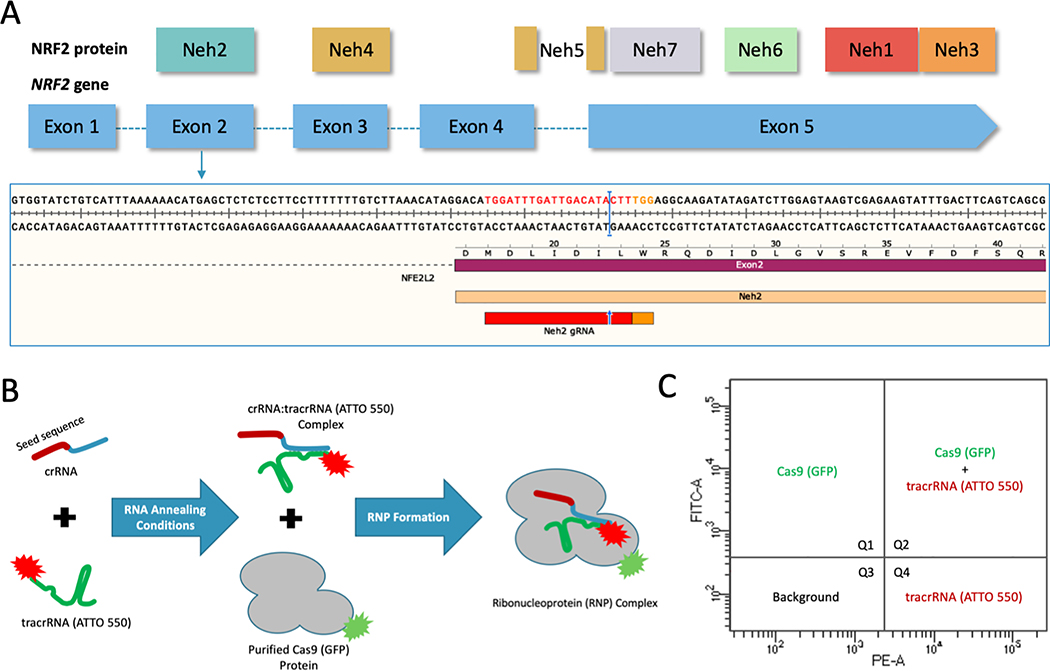
Figure 1.
(A) CRISPR design and NRF2 sequence target. Structural domains of the NRF2 protein aligned to the exons of the NRF2 gene. CRISPR/Cas9 was designed to target the beginning of exon 2 using the gRNA shown in red and the PAM sequence in orange with the cleavage site indicated by the blue arrow and bar. (B) CRISPR/Cas9 RNP assembly reaction using fluorescently labeled components. The crRNA contains the seed sequence (shown in red) designed to target exon 2 of the NRF2 gene. The blue region of the crRNA is the interaction domain for annealing with tracrRNA (shown in green), which is labeled with the ATTO-550 dye. The crRNA and tracrRNA are annealed in equimolar concentrations. The Cas9 protein, which is labeled with GFP, is added for complete RNP formation. (C) FACS analysis of fluorescently labeled RNP components. An example of the localization of each fluorescent component on a FACS dot plot. Quadrant 1 (Q1) would contain cells with GFP fluorescence. Quadrant 2 (Q2) would contain cells with both GFP and ATTO 550 fluorescence. Quadrant 3 (Q3) would contain cells that do not exceed background fluorescence. Quadrant 4 (Q4) would contain cells with ATTO 550 fluorescence.