Figure 7: eIF5A levels regulate pervasive non-AUG-initiated translation.
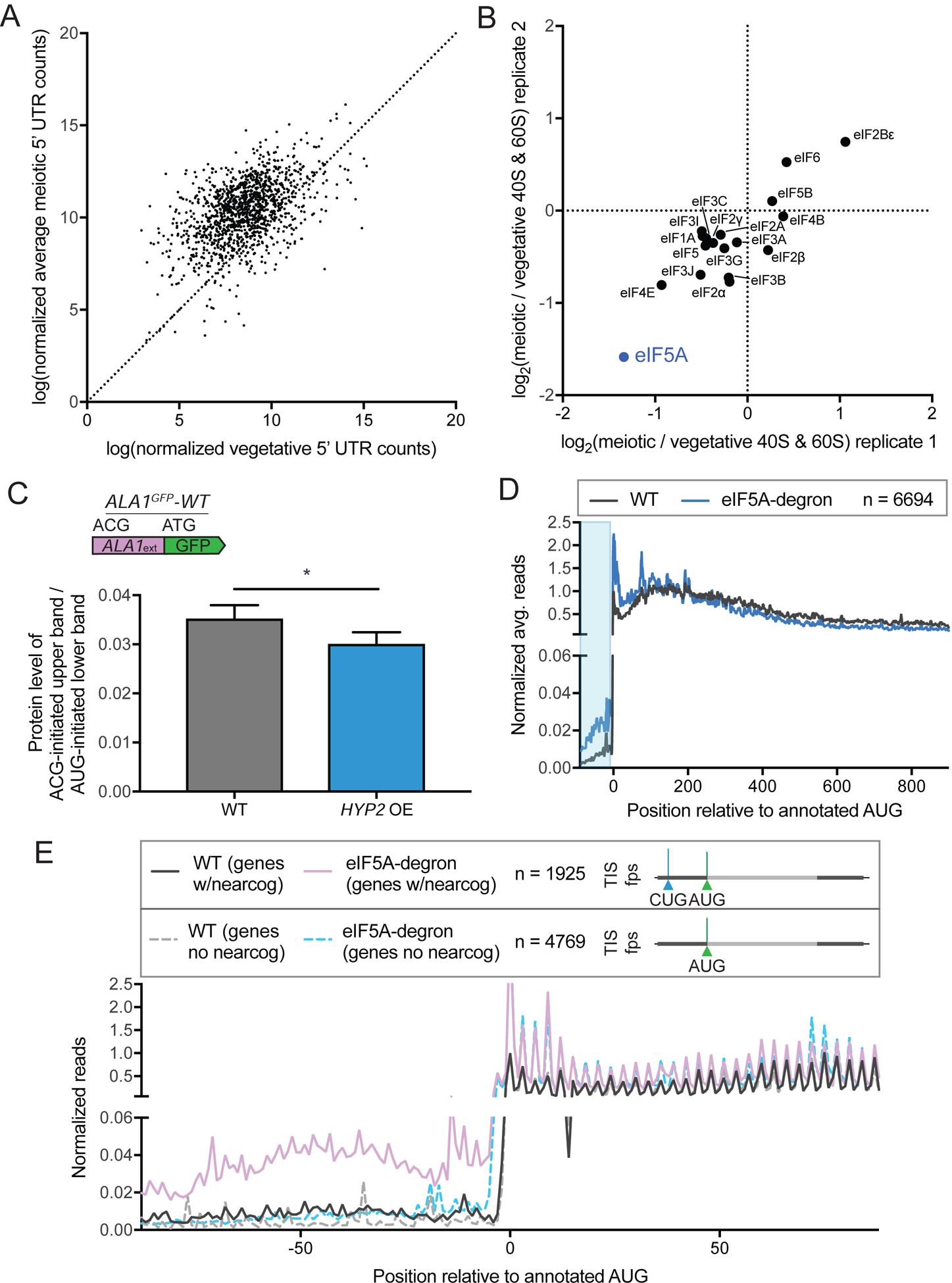
(A) Comparison of vegetative and average meiotic 5’ read density measurements.
(B) Enrichment of translation factors, comparing meiotic and vegetative samples for two replicates, determined by quantitative mass spectrometry of 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits isolated by sucrose gradient centrifugation of cell extract from meiotic and vegetative cells.
(C) Western blot quantification of ALA1GFP-WT reporter in meiosis with copper induction in strains containing or lacking a copper-inducible overexpression (OE) HYP2 allele. Non-AUG-initiated GFP upper band protein is normalized to AUG-initiated GFP lower band protein, which runs as a doublet. Both bands were used for quantification. The decrease seen with HYP2 OE is significant (p < 0.0146, 4 replicates).
(D) Metagene plot of normalized average reads from WT (black) and eIF5A-degron (blue) samples, 100 nt upstream and 900 nt downstream of annotated AUG start codons for all genes (n = 6694). Reads are normalized to WT at position zero and averaged across three nucleotides. Ribosome profiling data was re-analyzed from a previous study (Schuller et al., 2017). The area boxed in blue highlights the increased reads seen for the eIF5A-degron relative to WT in 5’ leader regions.
(E) Metagene plot around annotated start codons comparing genes with 5’ near-cognate-initiated ORFs annotated by ORF-RATER (n=1925, WT (genes w/nearcog): solid black and eIF5A-degron (genes w/nearcog): solid purple) and genes that do not contain 5’ near-cognate-initiated ORFs (n=4769, WT (genes no nearcog): dotted gray and eIF5A-degron (genes no nearcog): dotted light blue). Increased reads in the 5’ region are seen only in the eIF5A-degron samples for genes containing ORFs translated from near-cognate start codons in 5’ regions, based on TIS-profiling.
