Figure 5.
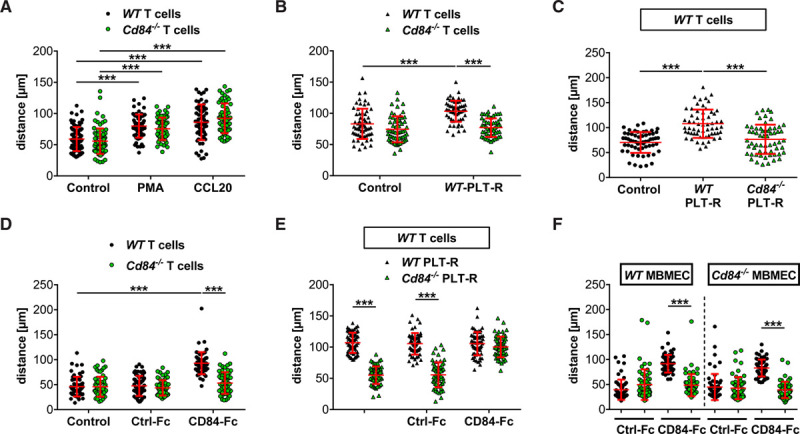
Soluble CD (cluster of differentiation) 84 promotes CD4+ T-cell migration.
A, Migrated distance of CD4+ WT and Cd84−/− T cells treated with vehicle, phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), or CCL20 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 20). B, WT and Cd84−/− CD4+ T-cell migration in response to stimulation with WT platelet-releasate (PLT-R) compared with vehicle (control). C, WT CD4+ T-cell migration in response to stimulation with WT or Cd84−/− PLT-R compared with control. D, Migrated distance of CD4+ WT and Cd84−/− T cells treated with vehicle, recombinant control-Fc, or CD84-Fc (recombinant soluble CD84 fused to the Fc part of human IgG1) protein. E, WT CD4+ T-cell migration in response to stimulation with WT or Cd84−/− PLT-R in the presence of control-Fc or recombinant CD84-Fc protein. F, Migrated distance of CD4+ WT and Cd84−/− T cells treated with control-Fc or CD84-Fc on primary murine brain microvascular endothelial cells (MBMECs) of WT or Cd84−/− mice. Each dot represents the migrated distance over 30 min of one CD4+ T cell (n=59–80 cells per group of 3–4 independent experiments). Horizontal red lines correspond to the mean and SD. Statistical significances analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn multiple comparison test, the exact test n-numbers and P are listed in Table VI in the Data Supplement. ***P<0.001.
