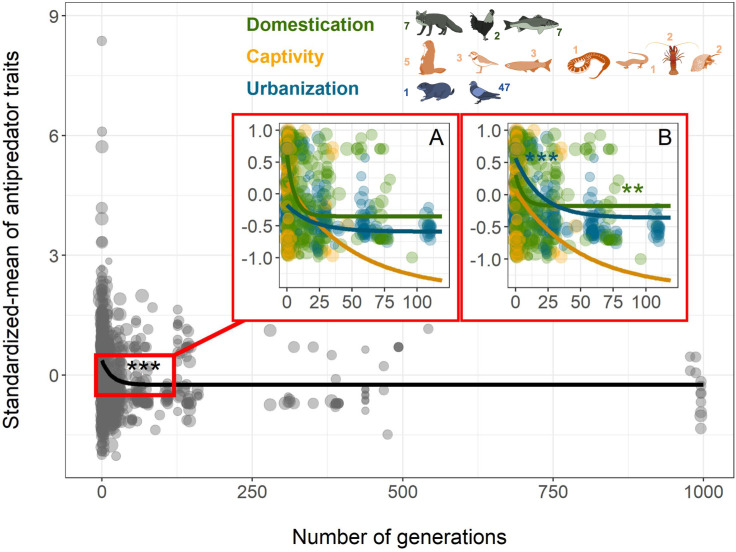
Fig 1. In multiple species, interactions with humans reduce the overall mean of antipredator traits over time, black line (all contexts).
(A) Lines correspond to the best inverse model fitting the data using the cma-es function. (B) Lines correspond to the best inverse model with the outputs (slopes and intercepts) of the MCMCglmm model for the mean. Dot size is proportional to the log-transformed number of replicates used in each study. “***” indicates significant p-value < 0.001 and “**” significant p-value < 0.01 of the inverse slopes with the MCMCglmm model (S1 Table). The number associated with each animal indicates the number of species in each of the following taxa: Mammals, Birds, Reptiles, Fish, Amphibians, Arthropods, and Mollusks. All data and R code supporting the figure are available in S1C Data. Species design: Pierre Lopez (MARBEC). cma-es, covariance matrix adapting evolutionary strategy; MARBEC, Marine Biodiversity, Exploitation and Conservation; MCMCglmm, Markov chain Monte Carlo generalized linear mixed model.