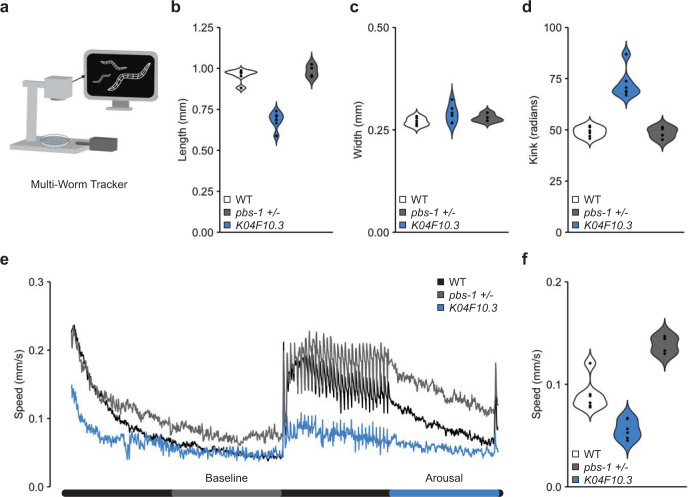
Fig 4. Deletion alleles of pbs-1 and K04F10.3 generated via peel-1-DMS selection reveal homozygous lethal and heterozygous behavioral phenotypes.
(A) Schematic of the Multi-Worm Tracker machine vision phenotyping system. A high-resolution camera records a plate of worms while the Multi-Worm Tracker software creates comprehensive digital representations of the worms in real time from which multiple phenotypes are later computationally extracted offline. The Multi-Worm Tracker also coordinates delivery of stimuli, e.g. the mechanosensory stimuli delivered to the plates via a push solenoid used here. (B) Worm length across genotypes. Each dot represents the mean of an independent plate replicate. Each plate consists of 20–100 worms. (C) Worm width across genotypes. Each dot represents the mean of an independent plate replicate. Each plate consists of 20–100 worms. (D) The degree of body posture kink (in radians) across genotypes. Each dot represents the mean of an independent plate replicate. Each plate consists of 20–100 worms. (E) Mean absolute movement throughout the tracking session. pbs-1 heterozygotes display initially normal locomotion speed and prolonged arousal following mechanosensory stimuli. (F) Quantification of aroused movement speed in the period following mechanosensory stimulation across genotypes. Each dot represents the mean of an independent plate replicate. Each plate consists of 20–100 worms. WT = PD1074 wild-type control, K04F10.3 = K04F10.3(gk5669), pbs-1 +/- = pbs-1(gk5673)/+.