Figure 1.
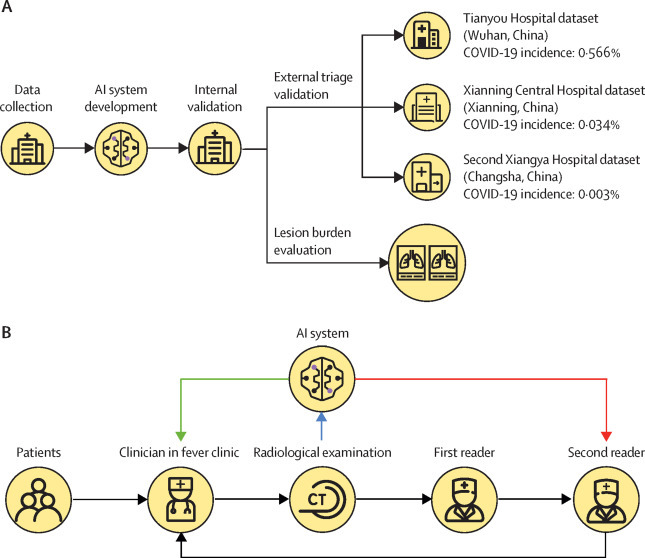
Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm to provide rapid triage in fever clinics and to automatically analyse lung opacities on the basis of chest CT scans
(A) Overview of the development and validation of the algorithm. (B) Evaluation of triage efficiency; black lines show the standard workflow in Chinese fever clinics; after a patient's CT examination is completed, a first reader drafts a radiology report in a first-in-first-out order and then a second radiologist revises and approves the first reader's report before sending it to a fever clinician; after receiving the radiological report the fever clinician decides whether the patient qualifies as a suspected case and should receive RT-PCR testing; we proposed that through directly notifying either the second radiologist (ie, scan-to-second-reader triage; red line) or the fever clinician (scan-to-fever-clinician triage; green line) of suspected cases triaged by AI, the workflow in fever clinics could be expedited. AI=artificial intelligence.
