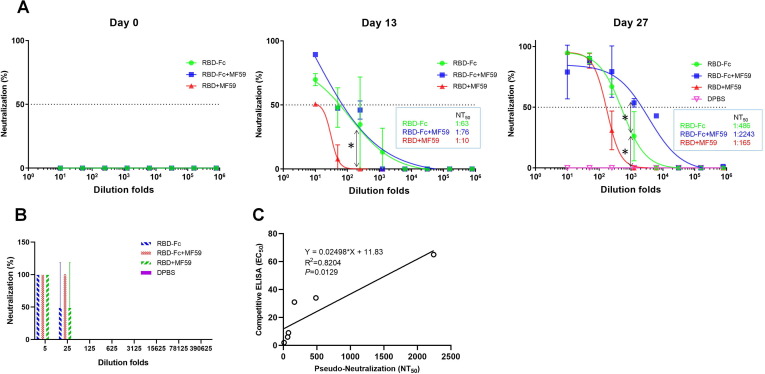
Fig. 3.
Potent neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus (A) and live virus (B) by mouse serum, correlation analysis for pseudo-neutralization and competitive ELISA (C). (A) Pseudoviruses were pre-incubated with serially diluted serum and then used to infect 293T-ACE2 cells. 24 hrs later, luciferase activities in cell lysates were recorded. 50% neutralizing antibody titers (NT50) was obtained by non-linear fitting of plots of neutralization against serum dilution folds in Graphpad Prism 7. (B) Neutralization of live virus by a microneutralization assay. Virus-induced cytopathic effects (CPE) were observed under the microscopy. The neutralization capacity (NT100) was expressed as the lowest dilution folds capable of completely preventing virus induced CPE in 100% of the wells. Experiments were performed in duplicate and the error bars denote ± SD, n = 2. Statistical significance was defined as *: P < 0.05. (C) Correlation analysis between pseudo-neutralization antibody titers (NT50) and competitive ELISA (EC50) for sera of day 13 and day 27. Correlation and linear regression analyses were performed in GraphPad Prism using Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Statistical significance was calculated using the two-tailed test. The dashed lines indicate the standard deviations of the linear regression plots.