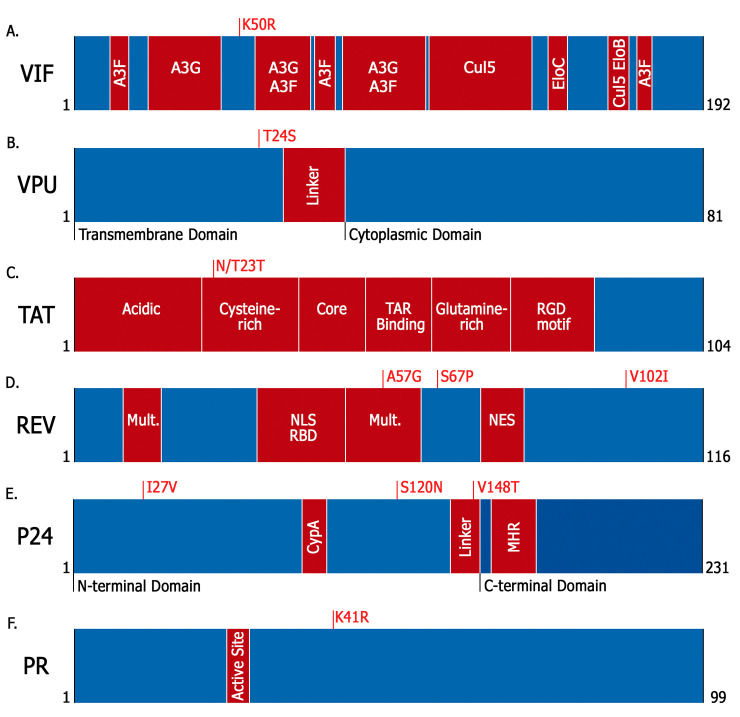
Fig 2. Mapping of the identified AAs between BCAR and BPANDEMIC on the accessory, regulatory and structural HIV-1 proteins.
For all proteins, their functional domains are represented; (A) Vif: regions responsible for the binding to APOBEC3G (A3G), APOBEC3F (A3F), Cullin 5 (Cul5), Elongin B (EloB), and Elongin C (EloC); (B) Vpu: the transmembrane domain, the cytoplasmic domain, and the linker region between them; (C) Tat: the N‐terminal acidic domain, the cysteine-rich domain, the hydrophobic core domain, the TAR binding domain, the glutamine-rich domain, and the RGD motif; (D) Rev: the RNA binding domain (RBD), that also functions as a nuclear localization signal (NLS), the nuclear exporting signal (NES), and sequences responsible for its multimerization (Mult.); (E) P24: the N-terminal domain and the C-terminal domain, connected by the inter-domain linker, the region mainly responsible for the interaction with cyclophilin A (CypA), and the major homology region (MHR); (F) Protease (PR): its active site.