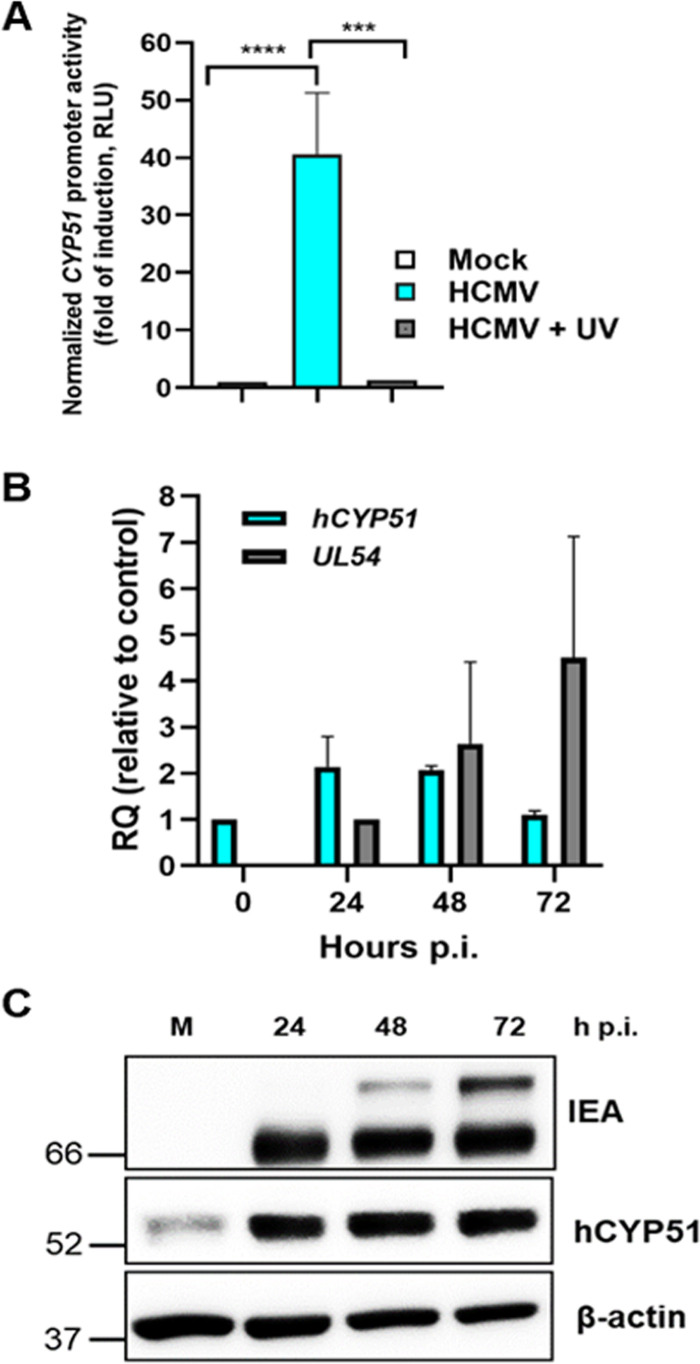
FIG 4.
hCYP51 expression is activated during HCMV infection. (A) Activation of the hCYP51 promoter in U-373 MG cells that were mock infected or infected with either HCMV AD169 or UV-inactivated HCMV. Data are expressed in relative luciferase units (RLU), which are the luciferase units normalized to the fluorescence units derived from the expression of the cotransfected eGFP reporter gene. Data are means ± SD from 3 independent experiments carried out in duplicate. Data were analyzed by a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison tests. ***, P ≤ 0.0001; ****, P < 0.0001. (B) Analysis of hCYP51 mRNA levels upon HCMV infection of HFFs determined by qPCR at the indicated times. The mRNA levels of UL54 were detected as a control for the progression of the infection at 24 and 48 h p.i. mRNA levels were normalized to cellular GAPDH, and gene expression was reported as relative quantification (RQ) compared to calibrator sample (mock-infected cells for hCYP51 and HCMV-infected cells at 24 h p.i. for UL54). Data are means and SD from 3 independent experiments carried out in duplicate. (C) Analysis of hCYP51 and viral protein expression during HCMV replication. Host hCYP51 protein and viral IE antigens (IEA) were detected by Western blotting both in mock-infected HFFs (M) and in HFFs infected with HCMV at an MOI of 0.5 PFU/cell at the indicated times p.i. Detection of host β-actin was used as a loading control. Molecular weights (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the left. An image from a representative experiment is shown.