FIG 5.
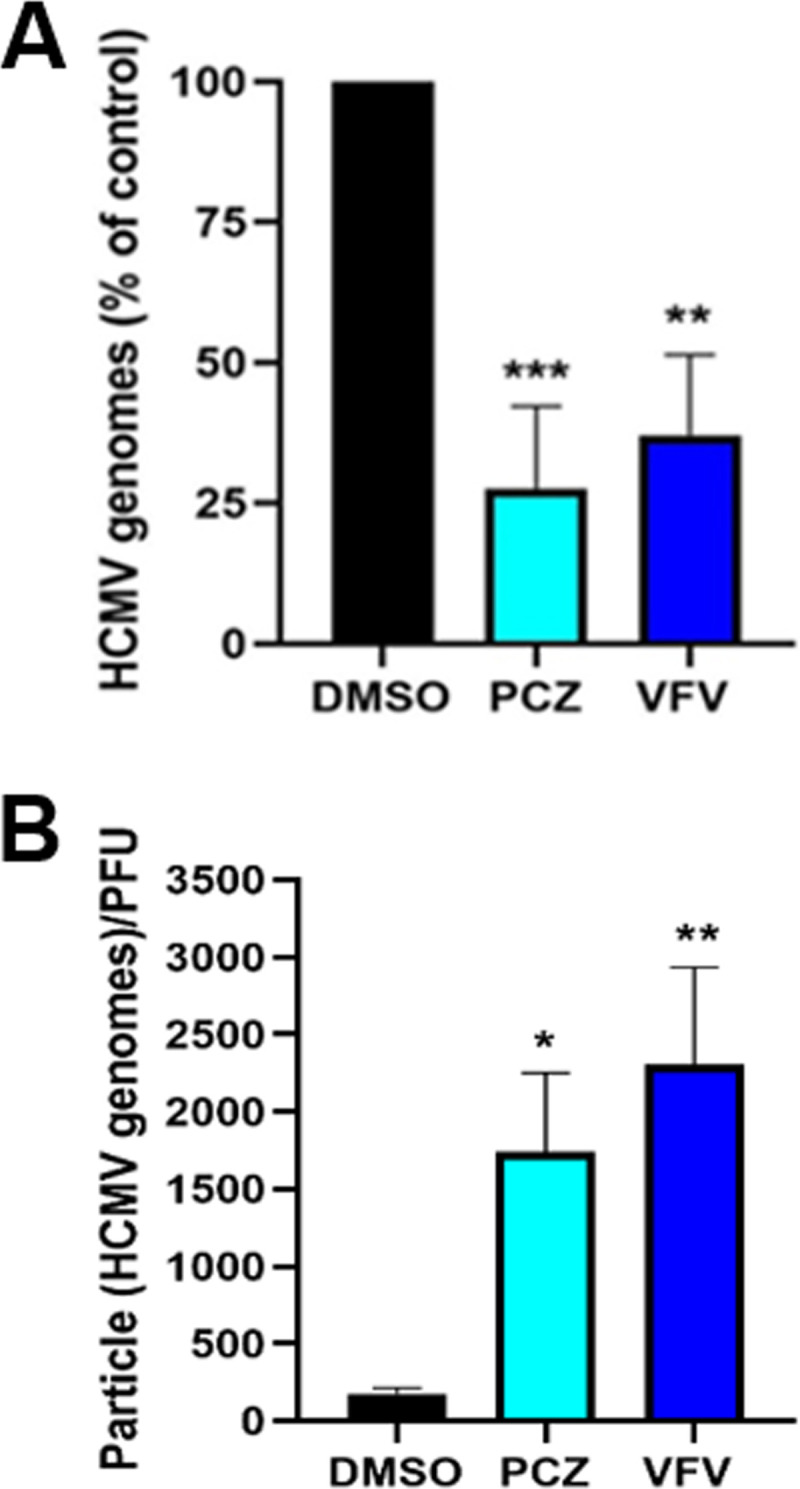
Effects of hCYP51 enzymatic activity inhibition on HCMV replication and infectivity. (A) Pharmacological inhibition of hCYP51 reduces the number of HCMV genomes. HFFs infected with HCMV at an MOI of 0.5 PFU/cell were treated with 10 μM PCZ or VFV or 0.1% DMSO as a control for 120 h. Numbers of HCMV genome copies in the supernatant of each sample were then determined by qPCR. Data are means and SD from 4 independent experiments carried out in quadruplicate. Data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test. ***, P < 0.001, and **, P < 0.005, compared to the control (DMSO-treated, infected sample). (B) Pharmacological inhibition of hCYP51 reduces the infectivity of viral particles. Particle-to-PFU ratios were obtained by dividing the number of HCMV particles collected from supernatants derived from HFFs infected at an MOI of 0.5 PFU/cell and treated with test compounds (determined by qPCR) by the viral titers obtained in the same sample volume (determined by titration on fresh monolayers). Data are means and SD from 3 independent experiments carried out in quadruplicate. Data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison tests. *, P < 0.05, and **, P < 0.005, compared to the control (DMSO-treated, infected sample).
