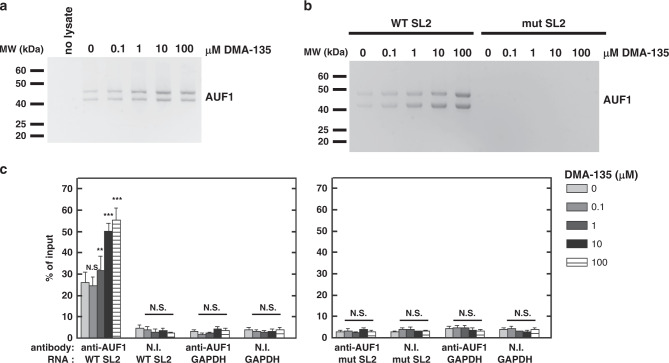
Fig. 7. Allosteric effects of DMA-135 within the cellular environment.
a Protein-biotinylated RNA pull-down experiments were performed to examine the effect of DMA-135 on the interaction between AUF1 and the EV71 SLII IRES domain. Biotinylated SLII was incubated with SF268 cell lysate to which was added the indicated concentrations of DMA-135. Streptavidin-linked beads were used to pull-down biotin-labeled SLII and its associated cellular proteins. Samples were analyzed by western blot using anti-AUF1 antibody. The experiment was performed twice yielding similar results. b Biotinylated wild-type SLII or the CCC-bulge mutant SLII were transfected into SF268 cells. Cells were cultured with various concentrations of DMA-135. Cell lysates were used for pull-down assays of SLII-associated proteins as described above. AUF1 bound to SLII RNA was detected by western blotting. The experiment was performed twice yielding similar results. c RIP assays for AUF1-EV71 Luc RNA interactions in cells. SF268 cells were transfected with RLuc-EV71 5′UTR-FLuc RNA, harboring the wild-type SLII, or with CCC-bulge mutant SLII and cultured with various concentrations of DMA-135. Lysates were prepared and analyzed by ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation (RIP) with non-immune (NI) antibody or AUF1 antibody. Both input and immunoprecipitated materials were analyzed by qRT-PCR for EV71 RNA. NI, non-immune antibody. Mean values±standard deviations from three independent experiments (N = 3) are shown. P values were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; N.S., not significant.