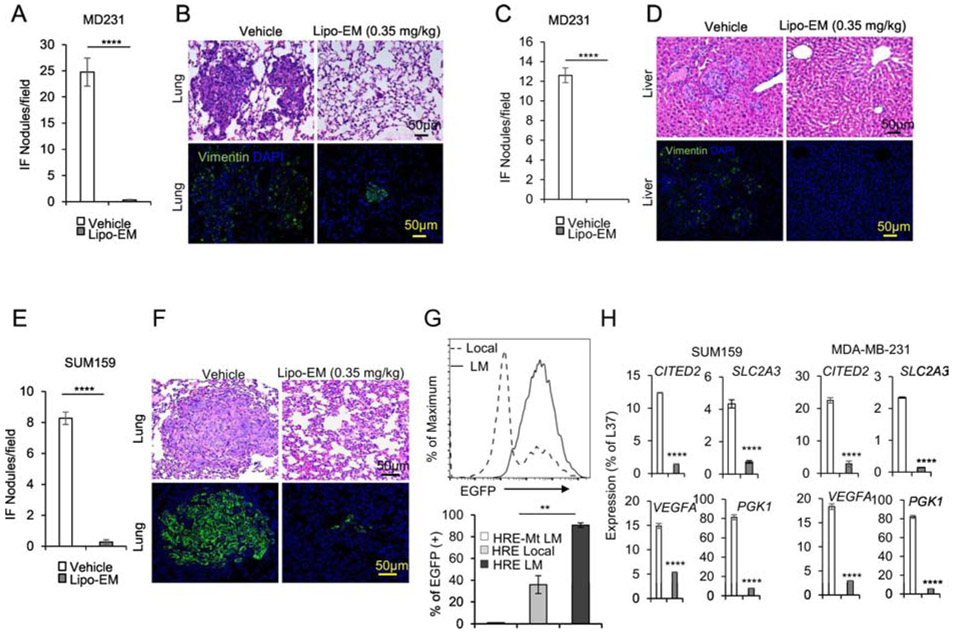
Figure 6.
Liposomal-echinomycin Eliminates Established Breast Cancer Metastases A-G) NSG mice were injected with 1.0x106 MDA-MB-231 or SUM-159 cells. Tumors measuring 5x5 mm were surgically resected, and the mice were treated with empty liposomes or liposomal-echinomycin 0.35 mgkg−1 (n=7/group), once every three days for 5 doses starting day 7 post-surgery. Mice were euthanized 25 days after surgery, and fixed lung and liver tissues were H&E or anti-human Vimentin stained to quantify metastasis. Representative H&E staining (B, D, F, top panels) and immunofluorescence staining (B, D, F, bottom panels) are shown for lung (B, F) and liver (D) tissues for MDA-MB-231 (B, D) or SUM-159 (D) xenograft mice. Summarized data corresponding to B, D, and F, are shown in A, C, and E, respectively, as mean number of human vimentin positive nodules ± SEM in the tissues. G) Higher HIF1α activity in lung-metastasized SUM-159 cells compared to primary SUM-159 cells. The primary tumor (Local) or lung-metastasis (LM) derived SUM159 cells were introduced with lentiviral HRE-EGFP reporter or mutated control (HRE-Mt) and cultured for 48 hrs. 2μg/ml puromycin was added and cells were cultured another 48 hrs prior to detection of EGFP expression by FACS. EGFP intensity histogram is shown for one representative mouse (Upper) and the summarized data for EGFP+ cells is shown (Lower). H) qPCR of HIF1α targets in lung-metastasized SUM-159 or MDA-MB-231 cells from liposomal-echinomycin or vehicle treated xenograft mice. Tumors were established according to the FSR method detailed in Figure 6A-G and 7 days after FSR the mice received liposomal-echinomycin 0.35 mgkg−1 or vehicle once every three days for three doses. On day 25 post-FSR, mice were sacrificed and primary or metastasized tumor cells were isolated and analyzed by qPCR.