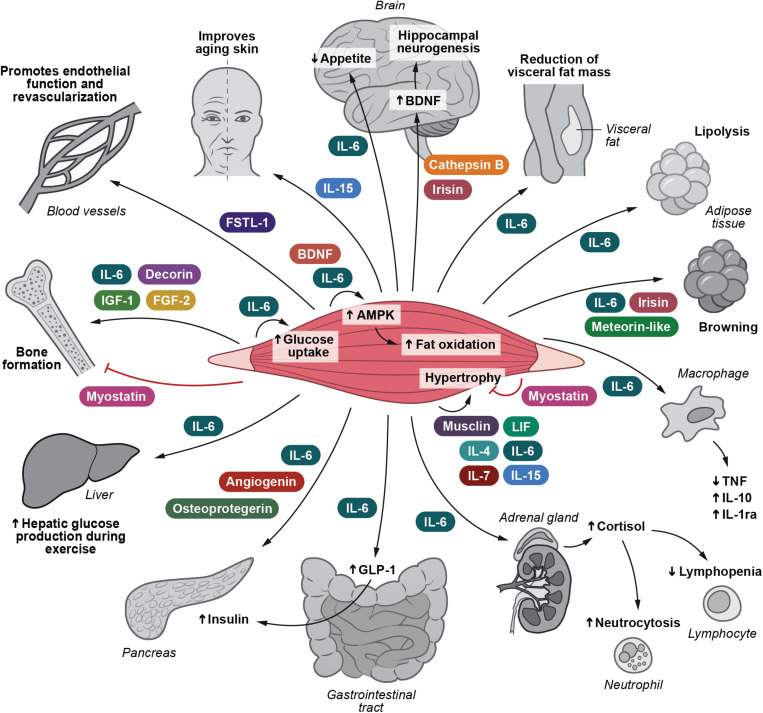
FIGURE 1.
I Irisin and Cathepsin B enhance BDNF production and thereby hippocampal neurogenesis. IL-6 inhibits appetite and stimulates lipolysis. IL-6 also plays a role in decreasing the amount of visceral fat. IL-6, irisin and meteorin-like are involved in turning white adipose tissue into a brown phenotype. IL-15 retards skin aging. IL-6, decorin, FGF-2 and IGF-1 positively influence bone formation. Myostatin negatively influence bone formation. Musclin, LIF, IL-4, IL-6, IL-7, and IL-15 are involved in mediating muscle hypertrophy, whereas myostatin obstructs muscle hypertrophy. IL-6 and BDNF stimulate AMPK activation and hence fat oxidation. IL-6 e stimulates glucose uptake and hepatic glucose output during exercise. IL-6 induces the expression of GLP-1 by the L cells of the intestine leading to enhanced insulin secretion. IL-6 exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting TNF production and by stimulating IL-1ra and IL-10 production. IL-6 enhances cortisol production, leading to neutrocytosis and lymphopenia. FSTL-1 has beneficial effects on endothelial function and revascularization of atherosclerotic blood vessels. Osteoprotegerin, angiogenin, and IL-6 possess beta-cell protective actions against inflammatory cytokines. AMPK, 5’-AMP-activated protein kinase; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; FGF-2, fibroblast growth factor 2; FGF-21, fibroblast growth factor 21; FSTL-1, follistatin-related protein 1; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor I; IL-1ra, IL-1 receptor antagonist; LIF, leukemia inhibitory factor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. Adapted with permission from Severinsen and Pedersen (2020).