Figure 9: Developmental increase in the innervation of lamina I projection neurons (PNs) by inhibitory DYN neurons.
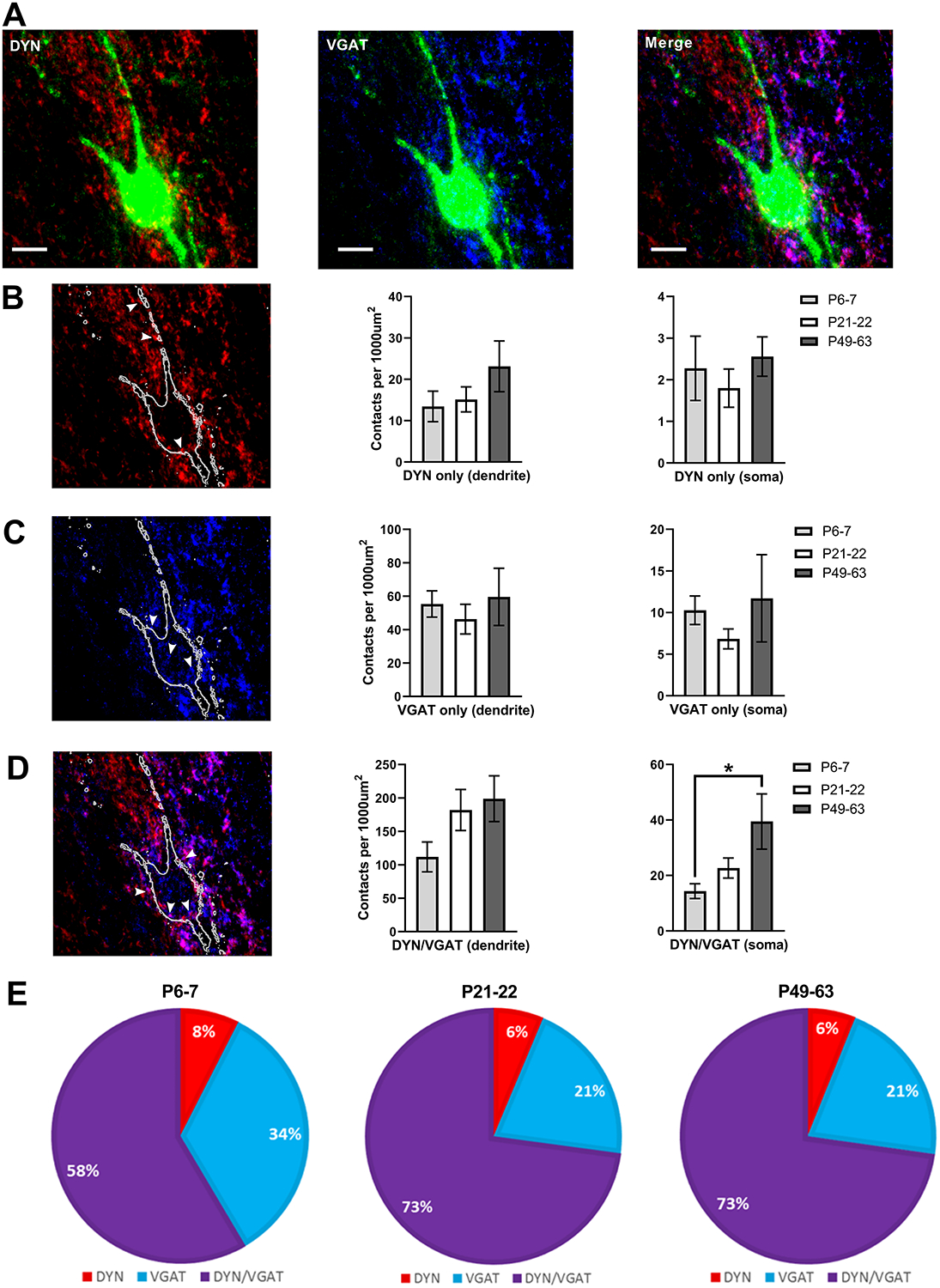
A) Images showing PNs labeled with antibody-based staining for the retrograde tracer CTB (green, all panels), DYN presynaptic terminals genetically labeled via synaptophysin-tdTOM (red, left and right panels), and inhibitory boutons labeled via antibody staining for VGAT (blue, middle and right panels; z-stack projection; scale bar = 10 μm). B) Left: z-stack projection image of presumed excitatory DYN terminals (white arrows) with synaptophysin-tdTOM expression but no VGAT immunoreactivity. Middle and right panels: Plot of the density of boutons in apposition to the dendrites and soma of PNs as a function of age, demonstrating that the density of excitatory DYN terminals onto PNs does not change throughout development (n = 8 neurons in each group). C) Left: Examples of inhibitory (i.e. VGAT+) boutons that do not originate from DYN-lineage neurons (i.e. are tdTOM-negative, white arrows). Middle and right panels: Quantification of DYN-negative inhibitory contacts onto PNs reveals no effect of age (n = 8). D) Left: Representative z-stack projection image of terminals expressing both VGAT and synaptophysin-tdTOM (white arrows), which represent inhibitory presynaptic terminals originating from DYN interneurons. While there was no statistically significant influence of age on the density of DYN/VGAT terminals apposed to PN dendrites (middle panel), there was a developmental increase in the density of inhibitory DYN contacts onto the somata of PNs (right panel; n = 8, H = 7.07, p = 0.03; Kruskal-Wallis test; *p < 0.05; Dunn’s multiple comparisons test). Please note the change in y-axis scale from panels B to D. E) The majority of inhibitory presynaptic terminals contacting PNs originate from DYN-expressing interneurons at all ages tested.
