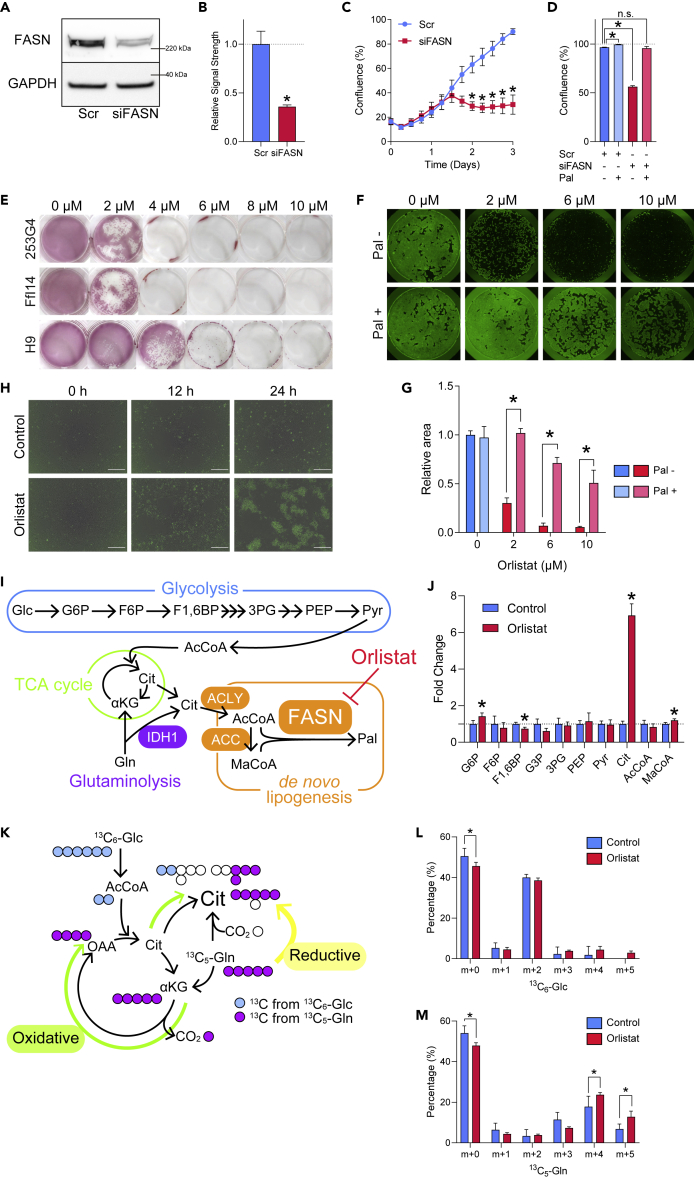
Figure 2.
Palmitic Acid Is Essential for the Survival of Undifferentiated hPSCs
(A) Representative western blot image for FASN and GAPDH of hiPSCs (253G4) after treatment with Scr or FASN siRNAs.
(B) Quantification of relative FASN content compared with GAPDH by western blot. Student's t test, n = 3.
(C) Growth of hiPSCs (253G4) treated with Scr RNA or FASN siRNAs. Holm-Sidak test was performed for each time point (n = 3).
(D) Confluence at 72 h after introduction of either Scr RNA or FASN siRNA to hiPSCs (253G4) with or without 50 μM Pal 24 h after introduction of RNAs. The same concentration of BSA (8.3 μM) was used as control. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett's test was performed with Scr RNA without Pal as control (n = 3).
(E) Alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining of hESCs (H9) and hiPSCs (253G4 and FfI14) treated with orlistat of the indicated concentrations for 72 h.
(F) Representative images of hiPSCs (253G4) cultured in 12-well plates stained with calcein AM after treatment with orlistat at the indicated concentrations for 24 h with or without 50 μM Pal. The same concentration of BSA (8.3 μM) was used as control for Pal.
(G) Quantification of hiPSC (253G4) relative cell area after treatment with orlistat at the indicated concentrations for 24 h, with or without 50 μM Pal. The same concentration of BSA (8.3 μM) was used as a control for Pal. Student's t test was performed to compare the presence and absence of Pal at each concentration of orlistat (n = 3).
(H) Detection of apoptosis by IncuCyte Caspase-3/7 Green Reagent staining following orlistat treatment. Scale bar, 200 μm.
(I) Metabolic pathway from glucose to Pal via glycolysis, glutaminolysis, TCA cycle, and de novo lipogenesis.
(J) CE-MS of intermediate metabolites in de novo FA synthesis from glucose after 3 h of 6 μM orlistat treatment. Data are normalized to controls. Student's t test was performed for each metabolite (n = 3). G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate, F1,6BP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; Pyr, pyruvate; Gln, glutamine, αKG, α-ketoglutarate; AcCoA, acetyl-CoA; MaCoA, malonyl-CoA; ACLY, ATP citrate lyase; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1.
(K) Metabolic pathway from glucose and glutamine to citrate via glycolysis, TCA cycle, and glutaminolysis. The major labeled form of citrate produced from 13C6-glucose, 13C5-glutamine via oxidative pathway, and glutamine via reductive pathway are m+2, m+4, and m+5, respectively.
(L) Percentage of labeled citrate formed after 1 h of orlistat treatment with 13C6-glucose. Student's t test was performed for each labeled form of citrate (n = 3).
(M) Percentage of labeled citrate formed after 1 h of orlistat treatment with 13C5-glutamine. Student's t test was performed for each labeled form of citrate (n = 3).
Data are presented as means ± SD; ∗p < 0.05.