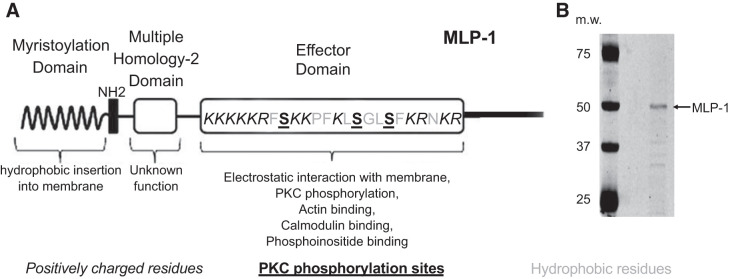
Fig. 1.
A: schematic diagram of myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS)-like protein-1 (MLP-1). Part of the MARCKS family of proteins, MLP-1 is the predominant MARCKS isoform in mouse kidney. MLP-1 consists of a myristoylation domain and a basic effector domain for which positive charge will electrostatically bind phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) and cause MARCKS or MLP-1 to associate with PIP2-rich lipid domains. The effector domain has multiple sites for PIP2 interaction (note positively charged residues) and sites for phosphorylation (note serine residues). MLP-1 functions as a reversible source of PIP2 at the membrane. The ability of MLP-1 to function as a PIP2-sequestering protein at the membrane is dependent on hydrophobic interactions between the myristoylation domain and the membrane and electrostatic forces between the effector domain and anionic lipids in the membrane. B: MLP-1 has a predicted molecular mass of ~21 kDa but migrates slowly and close to 52 kDa on SDS-PAGE gels probably due to its unusual positive charge. m.w., Molecular weight (i.e., molecular mass, in kilodaltons).