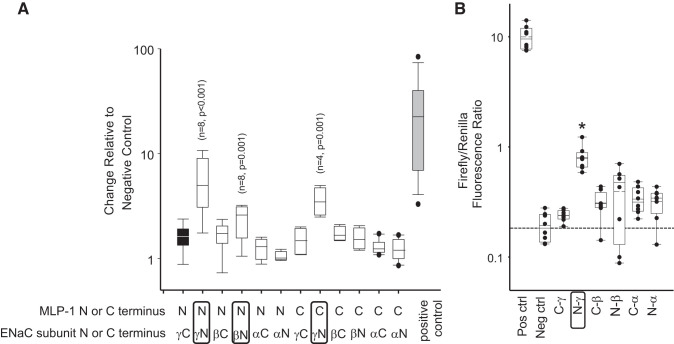
Fig. 8.
Mammalian Dual-Luciferase assay. In A, we found significant binding between NH2 (N)-terminal myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate-like protein-1 (MLP-1) and NH2-terminal γ-epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) relative to the negative control (black bar; Kruskal–Wallis 1-way analysis of variance on ranks). Similarly, there was moderate binding between NH2-terminal MLP-1 and NH2-terminal β-ENaC and between COOH (C)-terminal MLP-1 and NH2-terminal γ-ENaC but neither NH2- nor COOH-terminal α-ENaC in cells. In B, we examine binding of the multiple-homology domain 2 (residues 18–62 in MLP-1; Fig. 1) to cytosolic NH2- and COOH-terminal fragments of ENaC. Only NH2-terminal γ-ENaC bound significantly (*P < 0.001, Kruskal–Wallis 1-way analysis of variance on ranks; n = 6). Neg ctrl, negative control; Pos ctrl, positive control.