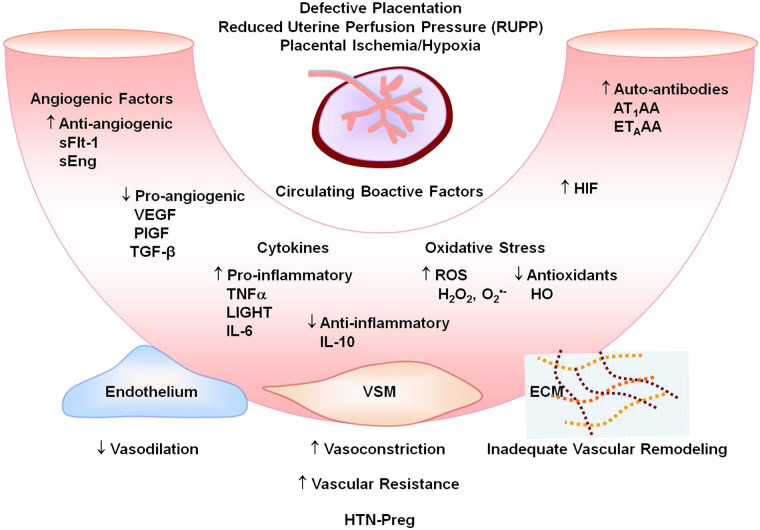
Fig. 4.
Circulating bioactive factors in preeclampsia. Defective placentation and placental ischemia lead to increased antiangiogenic soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) and soluble endoglin (sEng) and decreased proangiogenic VEGF, placental growth factor (PlGF) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β); increased proinflammatory cytokines and decreased anti-inflammatory cytokines; increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and decreased antioxidants such as hemeoxygenase (HO); and increased hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), angiotensin II type 1 receptor agonistic autoantibodies (AT1AA), and endothelin receptor type A (ETAR) agonistic autoantibodies (ETAAA). Circulating factors could target the endothelium leading to increased vasodilation, vascular smooth muscle (VSM) leading to increased vasoconstriction, and extracellular matrix (ECM) leading to inadequate vascular remodeling, increased vascular resistance, and hypertension in pregnancy (HTN-Preg) and preeclampsia.