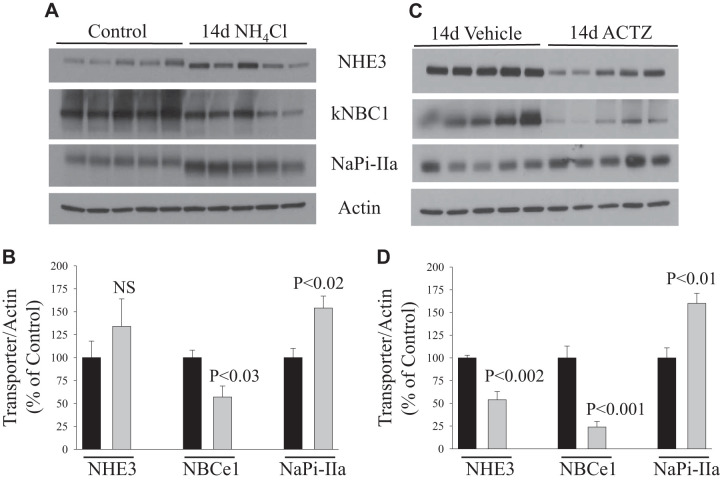
Fig. 7.
Response of acid-base transporters [Na+/H+ exchanger 3 (NHE3) and electrogenic basolateral Na+- cotransporter (NBCe1)] and phosphate transporter (NaPi-IIa) to acetazolamide (ACTZ) or NH4Cl loading for 2 wk. A and C: membrane fractions were isolated from the kidney cortex of rats treated with NH4Cl loading (A) or ACTZ (C) versus their respective control or vehicle treatment and were used for immunoblot analysis using specific antibodies for each protein. B and D: corresponding average means ± SE of the densitometry analysis of transport proteins in response to NH4Cl loading versus control (B) or in ACTZ-treated versus vehicle-treated rats (D). The abundance of these proteins was normalized to actin used for the control of gel loading. As shown, 2 wk of ACTZ caused a sharp downregulation of both NHE3 and NBCe1 but increased the abundance of NaPi-IIa. Except for NHE3, similar findings were seen in NH4Cl-loaded rats with normal acid-base status. n = 5 rats in each group. Each lane was loaded with 40 μg protein from the kidney cortex. NS, not significant.