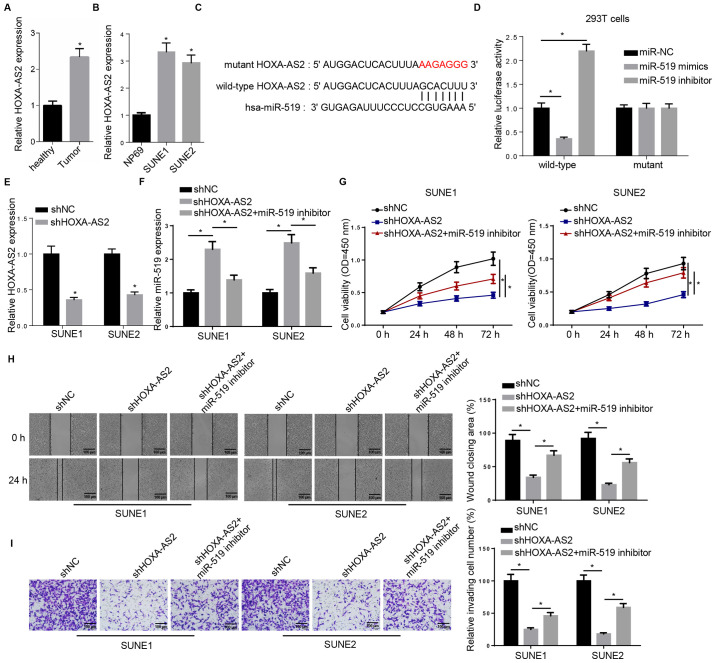
Figure 1.
miR-519 inhibitor rescues HOXA-AS2 knockdown-attenuated progression of NPC. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of HOXA-AS2 expression in NPC tumor tissues (n=15) and the adjacent healthy tissues (n=15). (B) RT-qPCR analysis of HOXA-AS2 expression in the normal nasopharyngeal epithelial cell line (NP69) and the NPC cancer cell lines (SUNE1 and SUNE2). (C) Bioinformatics analysis identified the binding site between miR-519 and HOXA-AS2. (D) Dual luciferase reporter assay demonstrated the direct interaction between miR-519 and HOXA-AS2. (E) RT-qPCR analysis of the expression of HOXA-AS2 in SUNE1 and SUNE2 cells transfected with shNC and shHOXA-AS2. (F) RT-qPCR analysis of miR-519 expression in cells transfected with shNC, shHOXA-AS2 and shHOXA-AS2 + miR-519 inhibitor. (G) MTT assay results of viability of cells transfected with shNC, shHOXA-AS2 and shHOXA-AS2 + miR-519 inhibitor at 0, 24, 48 and 72 h. (H) Wound healing assay and quantification demonstrated the migratory abilities of cells transfected with shNC, shHOXA-AS2 and shHOXA-AS2 + miR-519 inhibitor at 0 and 24 h. (I) Transwell invasion assay and quantification of the invasive abilities of cells transfected with shNC, shHOXA-AS2 and shHOXA-AS2 + miR-519 inhibitor. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P<0.05. miR, microRNA; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma; HOXA-AS2, HOXA cluster antisense RNA 2; sh, short hairpin RNA; NC, negative control; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; OD, optical density.