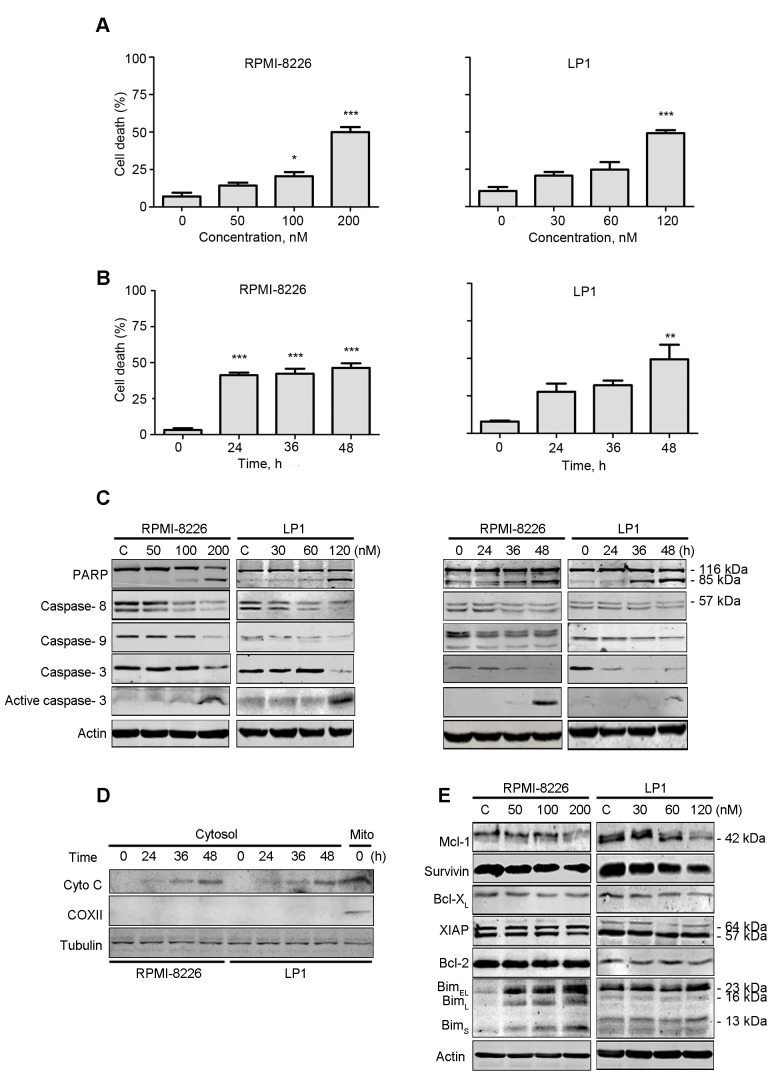
Figure 3.
PP induces apoptosis in MM. RPMI-8226 and LP1 cells were treated with PP at (A) escalating concentrations for 48 h or (B) a fixed concentration (200 nM for RPMI-8226 and 120 nM for LP1) for different durations. A trypan blue exclusion assay was performed to count viable cells. (C) Western blotting analysis of RPMI-8226 and LP1 cells treated with PP for 48 h or at a fixed concentration (200 nM for RPMI-8226 and 120 nM for LP1) for different durations. (D) RPMI-8226 and LP1 cells were exposed to the indicated levels of PP for 48 h; the levels of cytochrome c in the cytosolic fractions were monitored by western blotting. COXII served as a mitochondrial indicator to exclude the contamination of cytosolic fraction by mitochondria. (E) Western blotting analysis of apoptosis-associated proteins in RPMI-8226 and LP1 cells upon treatment with PP. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; compared with the control. PP, pyrvinium pamoate; MM, multiple myeloma; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; COXII, cyclooxygenase 2; BclXL, Bcl extra large; Bim, interacting mediator of cell death; XIAP, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein; Mcl-1, myeloid cell leukemia 1.