Figure 1.
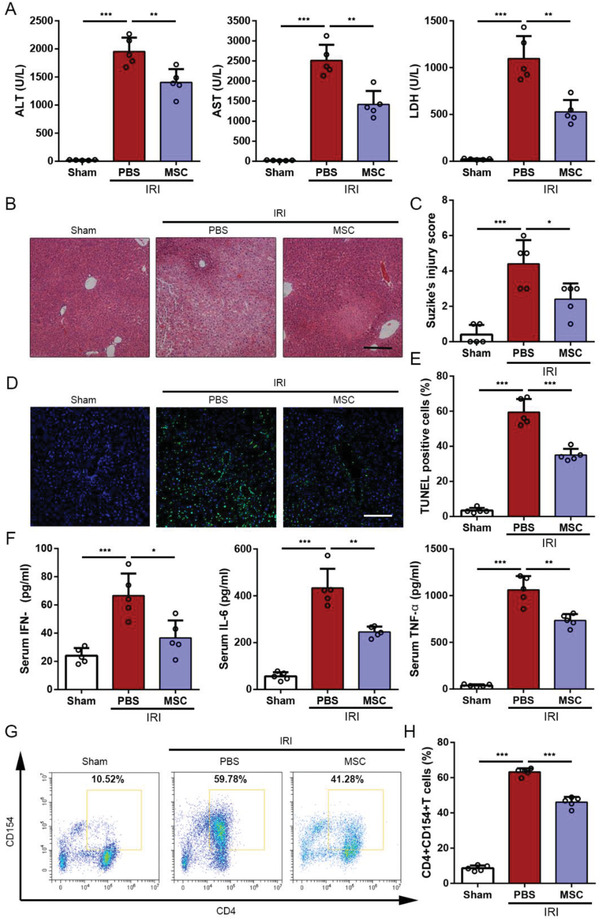
Effects of UC‐MSCs treatment on attenuating injury and suppressing CD154 expression on intrahepatic CD4+ T cells in the mouse liver IRI model. Mice that underwent liver IRI and were treated with UC‐MSCs or PBS were sacrificed at 6 h after reperfusion. A) Serum ALT, AST, and LDH from normal control (Sham group), liver IRI mice and UC‐MSCs‐treated liver IRI mice were detected at 6 h after reperfusion. The data are expressed as the means ± SEMs (n = 5 per group). B) Representative sections of livers stained with H&E from three groups after different treatments (bar = 200 µm). C) The severity of liver injury was evaluated from histological section and scored according to Suzike's injury criteria. The data are expressed as the means ± SEMs (n = 5 per group). D,E) Representative sections from each group stained with fluorescent TUNEL (bar = 200 µm). Statistical analyses of the percent of TUNEL positive cells in each field. Data are presented as the means ± SEM (n = 5 mice per group). F) The levels of IFN‐γ, IL‐6, and TNF‐α in serum from each group were measured using ELISA assay. Data are presented as the means ± SEM (n = 5 mice per group). G,H) Flow cytometry analyses of CD4+CD154+ T cells in intrahepatic CD3‐positive mononuclear cells of each treatment group. Statistical analyses of the percent of CD4+CD154+ cells in each group. Data are presented as the means ± SEM (n = 5 mice per group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (all p values were obtained by one‐way ANOVA).
