Figure 2.
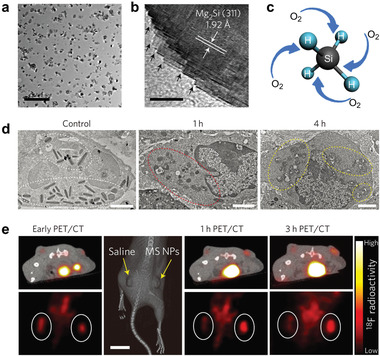
Magnesium silicide nanoparticles as a deoxygenation agent for inhibiting mitochondrial respiration of cancer cells. a) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of highly dispersed Mg2Si nanoparticles. Scale bar, 500 nm. b) High‐resolution TEM image showing the serrated edge of a single Mg2Si nanoparticle. Scale bar, 5 nm. c) Mechanism of deoxygenation reaction by Mg2Si nanoparticles. d) Bio‐TEM images of MCF‐7 cells treated with Mg2Si nanoparticles for prolonged durations, which show morphological damage of suffocated mitochondria. e) 18F‐labeled fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) images before and after different‐treatments showing a significantly enhanced hypoxia after Mg2Si nanoparticle (denoted MS NP in this figure) injection. Reproduced with permission.[ 10 ] Copyright 2017, the Authors, published by Springer Nature.
