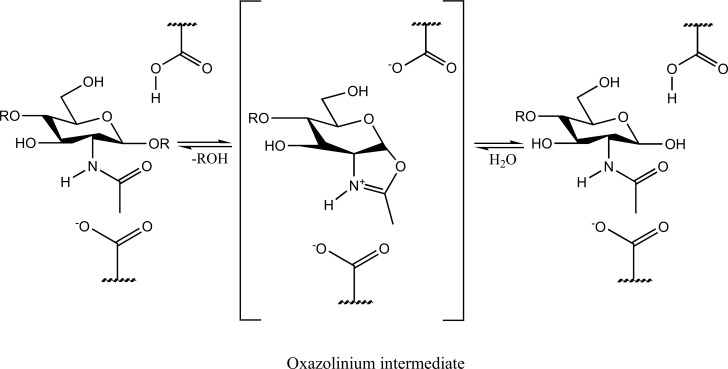
Fig. (1).
Mechanism of action of chitinases undergoing chitin hydrolysis. Here, R is β-1,-linked N-acetylglucosamine residue. Chitinases hydrolyze the glycosidic linkage of the repeating β -1,-linked N-acetylglucosamine-containing polymer chitin. The hydrolysis is accompanied with the formation of an oxazolinium intermediate followed by the degradation of chitin in simpler monosaccharides.