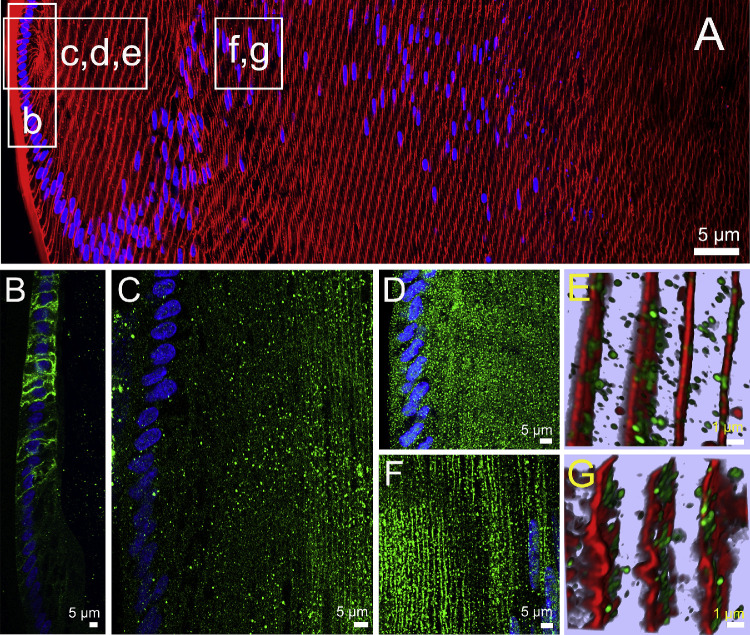
Figure 2.
Subcellular localization of lens AQPs in the efflux zone of rat lenses in the absence of zonular tension. (A) Image montage of the water efflux zone taken from an axial section of a rat lens that had been removed from the eye by first cutting the zonules and was then placed immediately into fixative. The section was labeled with the membrane marker WGA (red) and the nuclei marker DAPI (blue). Boxes indicate the areas from which the higher resolution two-dimensional images (B, C, D, F) or three-dimensional airy scan images (E, G) were taken from to investigate the subcellular distribution for each lens AQP (green). (B) AQP1 labeling is localized to the membranes of the epithelial cells but disappears as the epithelial cells differentiate into fiber cells. (C) AQP0 labeling was absent from epithelial cells but became apparently initially as diffuse punctate labeling as epithelial cell differentiated into fiber cells and in later stages of fiber cells differentiation was found strongly associated with the membranes of these deeper localised secondary fiber cells. (D) AQP5 labeling was initially associated with the cytoplasm in the epithelial cells and newly differentiated fiber cells being localized in cytoplasmic vesicles (E). (F) In deeper differentiating fiber cells ∼150 µm in from the capsule, AQP5 labeling became membranous and the number of cytoplasmic vesicles was dramatically reduced (G).