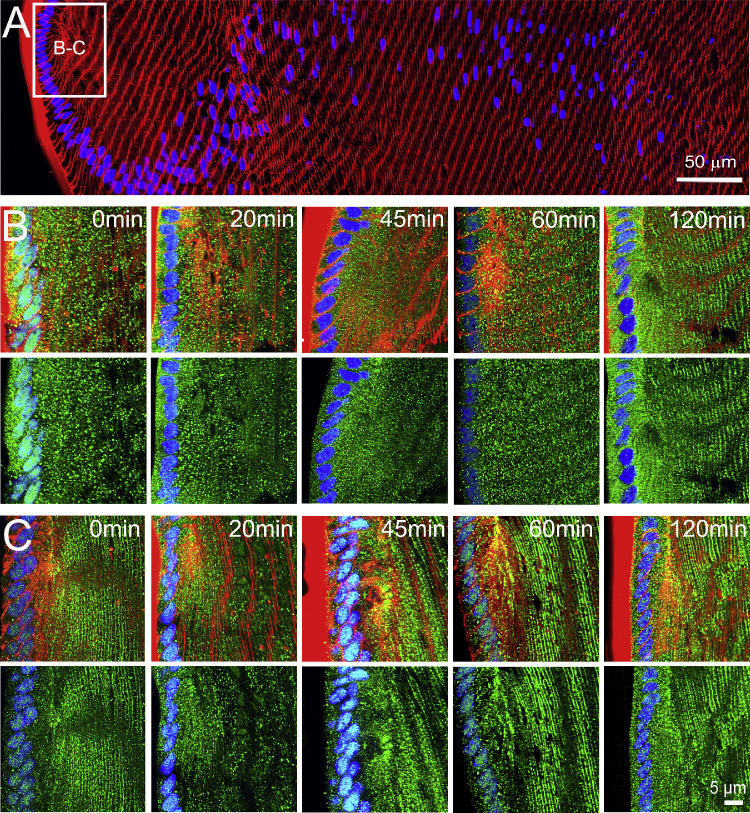
Figure 3.
Effects of mechanically altering zonular tension on the subcellular localization of AQP5 in the efflux zone of the rat lens. (A) Image montage of the water efflux zone taken from a representative axial section of a rat lenses labeled with the membrane marker WGA (red) and the nuclei marker DAPI (blue). The box indicates the area from which high-resolution images (B, C) were captured to monitor the time course of changes to the subcellular distribution of AQP5 (green) over a period of up to 120 minutes, in lenses that had been removed from the eye by cutting the zonules (B), or in lenses maintained in situ with their zonules intact (C). Top panels in B and C show nuclei, membrane, and AQP5 labeling, while bottom panels show only nuclei and AQP5 labeling. In lenses maintained in organ culture with their zonules cut (B), the subcellular localization of AQP5 changes from a cytoplasmic to a membranous labeling pattern over time. In lenses in which the zonular tension is maintained (C), AQP5 labeling is associated with the membrane, and this labeling does not change over time in organ culture.