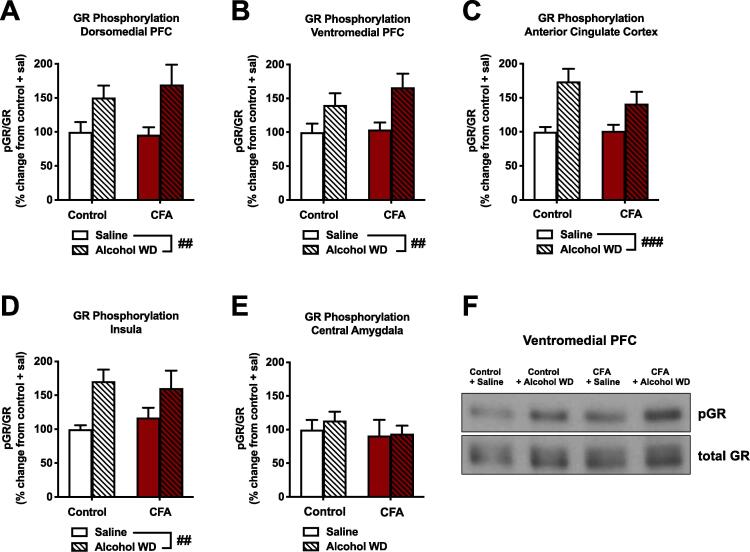
Fig. 5.
The interaction of chronic inflammatory pain and binge alcohol withdrawal on glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation. Binge alcohol exposure and withdrawal increased GR phosphorylation (Ser232 in both control and CFA-treated animals in the (A) dorsomedial PFC, (B) ventromedial PFC, (C) anterior cingulate cortex, and (D) insula (##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 main effect of group). (E) In the CeA, there was no effect of CFA treatment or acute alcohol WD on GR Ser232 phosphorylation. (F) Representative Western blots of pGR and total GR in the ventromedial PFC. Data were analyzed using 2-way RM ANOVA and Sidak's multiple comparisons test (B) or 2-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc tests (C-G). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Saline control + saline, solid white (n = 9); Saline control + acute alcohol WD, white striped (n = 11); CFA + saline, solid red (n = 9); CFA + acute alcohol WD, red striped (n = 9). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)