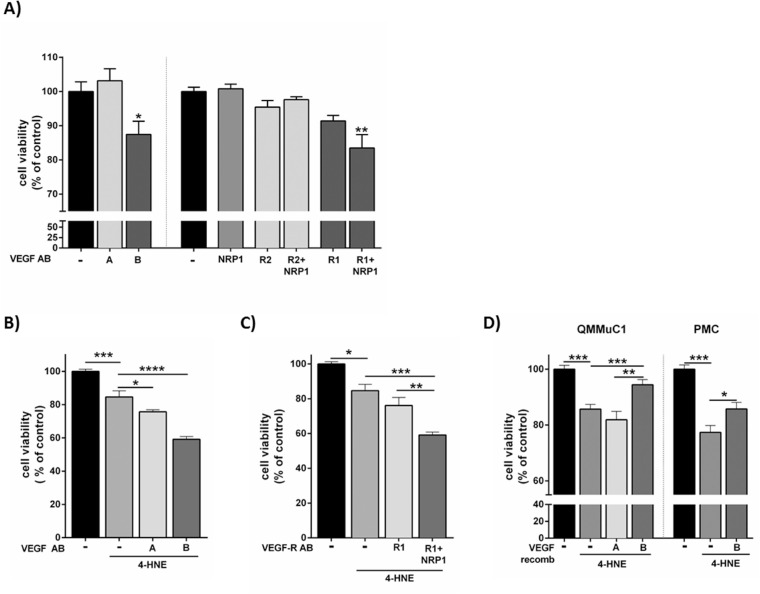
Figure 3.
The effect of VEGF-B and its receptors on Müller cell viability under oxidative stress and hypoxic conditions. (A) Effect of the neutralization of VEGF-A and its receptors (VEGFR2 and NRP1) and VEGF-B and its receptors (VEGFR1 and NRP1) on QMMuC-1 Müller cell viability under hypoxic conditions (1% O2 for 72 hours). *P < .05; **P < .01 compared with control (hypoxia only), one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test. (B) Effect of VEGF-A or VEGF-B neutralization on 4-HNE–induced QMMuC-1 Müller cell viability. C, Effect of the neutralization of VEGFR1 and NRP1 on QMMuC-1 and their receptor (VEGFR1 and NRP1) on 4-HNE–induced QMMuC-1 damage. (D) The effect of recombinant VEGF-B and VEGF-A on 4-HNE–induced cell death in QMMuC-1 and PMC Müller cells. The viability of cells was determined by Alamar Blue methods. (A) n = 5–9, (B and C) n = 4–6, (D) n = 5–10 per group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005 and ****P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Newmann-Keuls post hoc test. Antibody, AB. A and B are VEGF-A and VEGF-B respectively. R1 and R2 are VEGFR1 and VEGFR2. Anti-VEGF-A, VEGFR2 500 ng/mL and 10 µg/mL, respectively; NRP1 antibody, 30 µg/mL; VEGF-B and VEGFR1, 500 ng/mL and 10 µg/mL, respectively; recombinant VEGF-A and VEGF-B, 100 ng/mL; 4-HNE 20 µM.