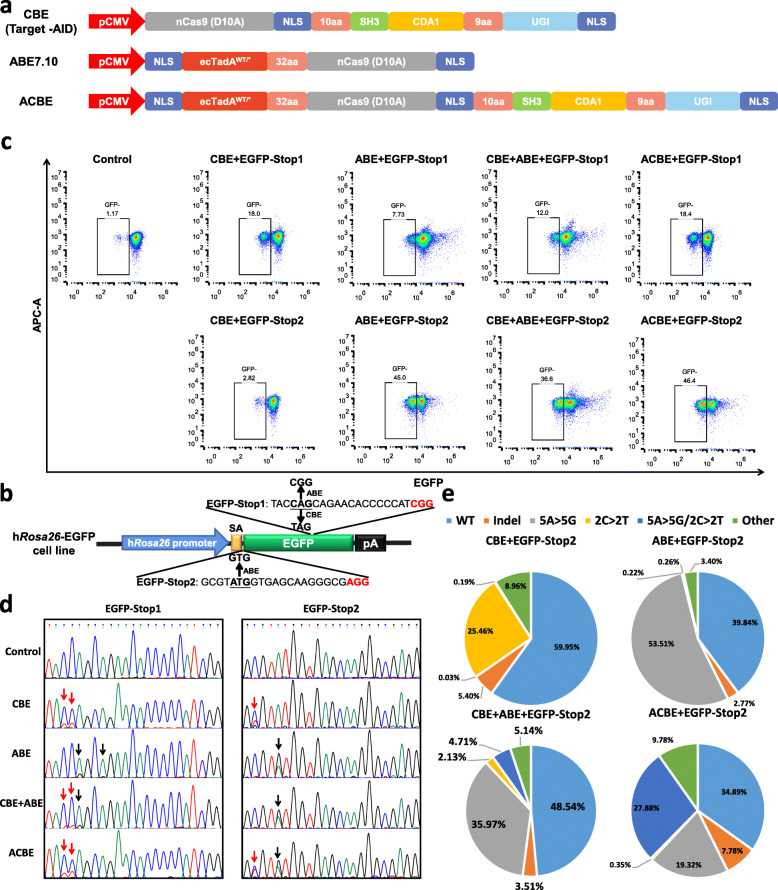
Fig. 1.
Simultaneous C-to-T and A-to-G base substitutions induced by the ACBE system. a Architectures of the dual-function base editing system, ACBE, and individual base editing systems, namely Target-AID and ABE7.10. ecTadAWT/*, a heterodimer of an evolved Escherichia coli TadA and a wild-type TadA; aa, amino acid; NLS, nuclear localization signal; UGI, inhibitor of uracil DNA glycosylase. b Schematic of the HEK293-EGFP reporter cell line and two targeting sgRNA (EGFP-Stop1 and EGFP-Stop2), which could induce a stop codon and mutation of start codon, respectively. c The representative results of flow cytometry showed the proportion of EGFP-negative cells edited by different base editors with the corresponding sgRNA. Three independent experiments were performed. d The representative Sanger sequencing results of the cell samples transfected with different base editors showed the target base substitutions in the targeting sites EGFP-Stop1 and EGFP-Stop2. The C-to-T and A-to-G substitutions were marked with red and black arrows, respectively. e The editing effects on the target site EGFP-Stop2 generated by the ACBE and CBE + ABE system. Different parts with various colors in the pie chart showed the frequencies of the corresponding mutation type