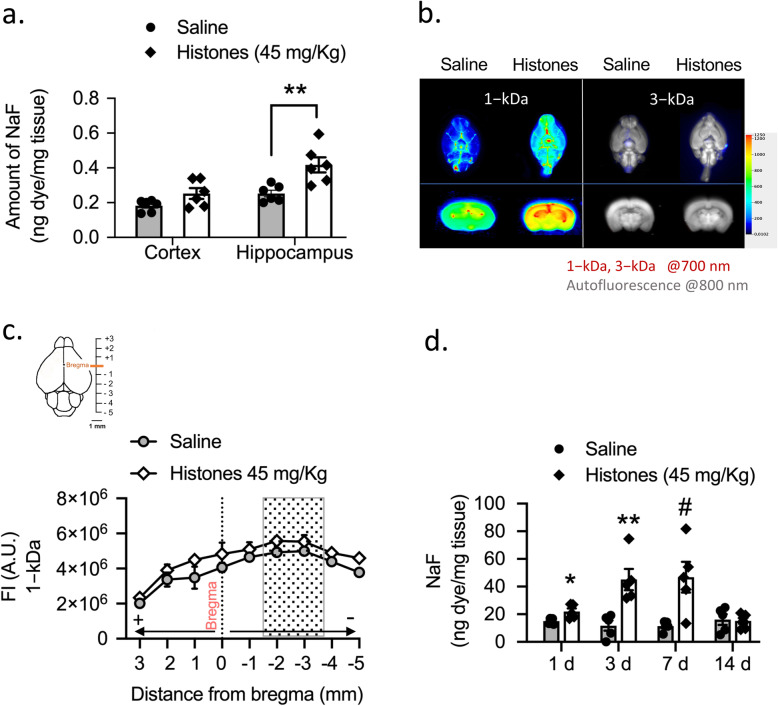
Fig. 3.
Circulating levels of extracellular histones increase BBB permeability. a Quantitative analysis showing NaFl uptake in cerebral cortex and hippocampus in saline- compared to histones-treated group. Mann–Whitney test; **P = 0.0043; Mean ± S.E.M.; n = 6 mice per group. b Representative NIR fluorescence images of the ventral whole-brains (upper) and coronal sections (bottom) across the hippocampus of saline- and histone-treated mice showing the distribution of 1-kDa and 3-kDa tracers within the brain. For images source data, see Supplementary Fig. 3a, b. c Quantification of whole-slide brain sections (+ 3 to − 5 mm from bregma) fluorescence intensity (AU, arbitrary units) of 1-kDa IRDye tracer in saline- and histone-treated mice. Mean ± S.E.M.; n = 3−4 mice per group. Gray box highlights coronal sections within the brain containing hippocampus region. d Time course of BBB permeability changes as measured by NaFl uptake in total whole brains. Mann–Whitney test; *P = 0.017. **P = 0.008; #P = 0.031 compared to saline group, same time point; mean ± S.E.M.; n = 5 mice per group