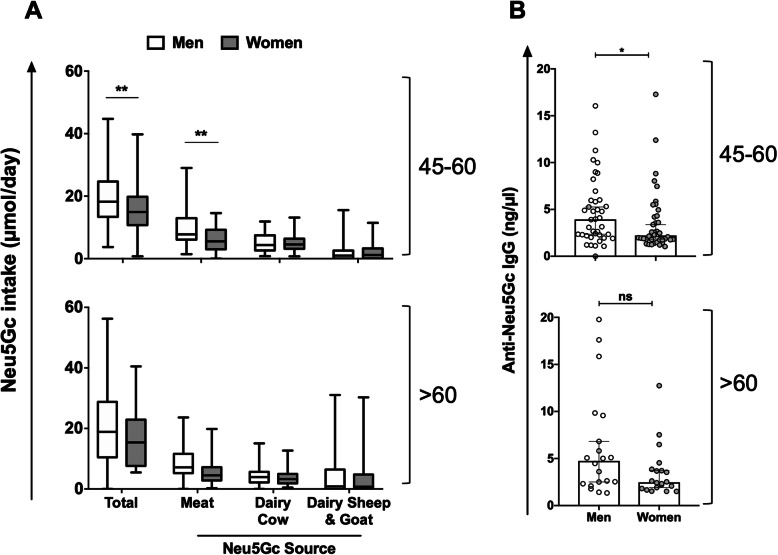
Fig. 3.
Distribution of daily Neu5Gc intake and anti-Neu5Gc IgG by age and gender. a Significantly higher total daily Neu5Gc intake in men compared to women (age 45–60; n = 40 per gender) mostly contributed from higher consumption of red meat. Similar trend in the group aged > 60 (n = 20 per gender; median and whiskers of min-max; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest; **p = 0.0015). b Overall anti-Neu5Gc IgG (by EIA) were significantly higher in men compared to women aged 45–60, with a similar trend in the group aged > 60 (median with 95% CI, Mann-Whitney test; *p = 0.0397; ns, p = 0.0822)