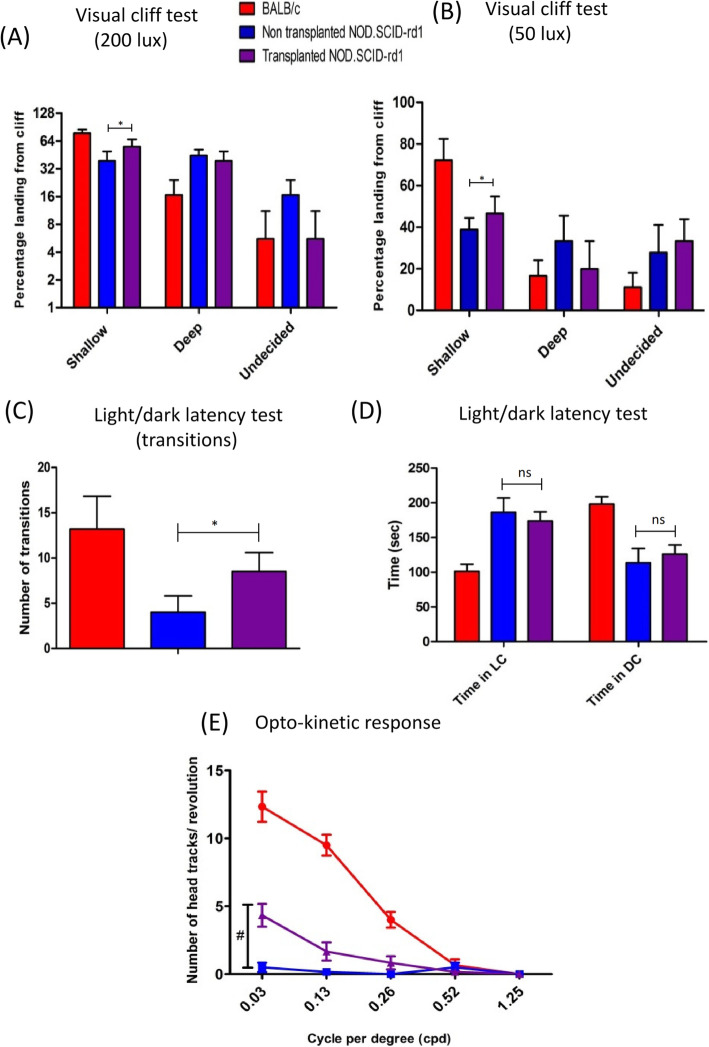
Fig. 6.
Functional analysis for vision rescue in host after transplantation of RNLCs in the retina. a The transplanted mice showed improved depth perception and stepped on the shallow side more number of times than deep side in both light (200 lx) and b dim (50 lx) conditions. c The light/dark latency test suggested that the transplanted animals spent comparable time in light chamber and that there was no noticeable change in their aversion to light as compared to non-transplanted animals. d The transplanted mice had an increased exploratory behaviour indicated by transitions between light chamber (LC) and dark chamber (DC) (n = 6). e The transplanted mice displayed significant increase in head tracks at 0.03 cycles per degree (cpd). It exhibited no significant change for the rest of the spatial frequencies (n = 6); *p < 0.05; #p < 0.001