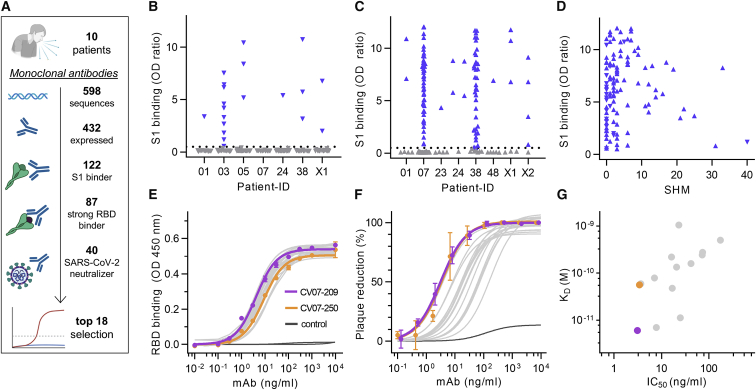
Figure 1.
Identification and Characterization of Potent SARS-CoV-2-Neutralizing mAbs
(A) Diagram depicting the strategy for isolation of 18 potently neutralizing mAbs (top 18).
(B) Normalized binding to S1 of SARS-CoV-2 for mAbs isolated from ASCs (inverted triangles; blue, S1-binding; gray, not S1-binding). OD, optical density in ELISA.
(C) Normalized binding to S1 of SARS-CoV-2 for mAbs isolated from S1-stained MBCs (triangles; colors as in B).
(D) S1-binding plotted against the number of somatic hypermutations (SHMs) for all S1-reactive mAbs.
(E) Concentration-dependent binding of the top 18 SARS-CoV-2 mAbs to the RBD of S1 (mean ± SD from two wells of one experiment).
(F) Concentration-dependent neutralization of authentic SARS-CoV-2 plaque formation by the top 18 mAbs (mean ± SD from two independent measurements).
(G) Apparent affinities of mAbs to RBDs (KD determined by surface plasmon resonance) plotted against IC50 of authentic SARS-CoV-2 neutralization.
See also Figures S1, S2, S3, S4, and S5 and Tables S1, S2, and S3.